Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase overexpression causes kynurenine-modification of proteins, fiber cell apoptosis and cataract formation in the mouse lens
- PMID: 19308046
- PMCID: PMC2722445
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.22
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase overexpression causes kynurenine-modification of proteins, fiber cell apoptosis and cataract formation in the mouse lens
Abstract
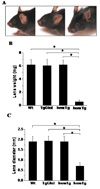
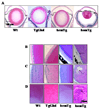
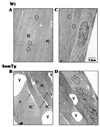
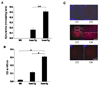
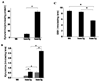
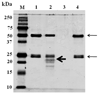
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is the first enzyme in the kynurenine pathway. The kynurenines formed in this pathway chemically modify proteins and cause apoptosis in cells. Evidence suggests that kynurenines and their protein modifications are involved in cataract formation, but this has yet to be directly demonstrated. We generated transgenic (Tg) mouse lines that overexpress human IDO in the lens. Homozygous Tg (homTg) lenses had higher IDO immunoreactivity, approximately 4.5 times greater IDO mRNA, and approximately 8 times higher IDO activity compared to lenses from hemizygous Tg (hemTg) animals. The kynurenine content was threefold higher in homTg than in hemTg but was not detected in wild-type (Wt) lenses. Kynurenine modifications were approximately 2.6 times greater in homTg than in hemTg or Wt. HomTg lenses had vacuoles in the epithelium and cortical fiber cells. Kynurenine modifications coincided with apoptosis in the secondary fiber cells of homTg lenses. Caspase-3 and caspase-9 activities were markedly higher in homTg than in hemTg and Wt. The glutathione content was approximately 36% lower in homTg compared to hemTg and Wt lenses. HomTg animals also developed bilateral cataracts within 3 months of birth. Together these data demonstrate that IDO-mediated production of kynurenines results in defects in fiber cell differentiation and their apoptosis and suggest that IDO activity is kept low in the lens to prevent deleterious effects by kynurenines.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by interferon-gamma in human lens epithelial cells: apoptosis through the formation of 3-hydroxykynurenine.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;42(9):1446-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 May 6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20435158 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle arrest by kynurenine in lens epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Dec;49(12):5466-75. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2374. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18676626 Free PMC article.
-
UVA light-excited kynurenines oxidize ascorbate and modify lens proteins through the formation of advanced glycation end products: implications for human lens aging and cataract formation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 13;289(24):17111-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554410. Epub 2014 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24798334 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptophan Metabolism in Obesity: The Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-1 Activity and Therapeutic Options.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:629-655. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_21. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287867 Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2; a new enzyme in the kynurenine pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;41(3):467-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18282734 Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is dysregulated in inflammation, and immune activation.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015 Jun 1;20(7):1116-43. doi: 10.2741/4363. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015. PMID: 25961549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Properties of Kynurenines: Density Functional Theory Calculations.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Nov 18;12(11):e1005213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005213. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27861556 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenine inhibits fibroblast growth factor 2-mediated expression of crystallins and MIP26 in lens epithelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jul-Aug;1802(7-8):609-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20478381 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by interferon-gamma in human lens epithelial cells: apoptosis through the formation of 3-hydroxykynurenine.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;42(9):1446-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 May 6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20435158 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable chromatographic assay for measuring of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) activity in human cancer cells.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):581-592. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1882451. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33541164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King NJ, Thomas SR. Molecules in focus: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:2167–2172. - PubMed
-
- Takikawa O. Biochemical and medical aspects of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-initiated L-tryptophan metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;338:12–19. - PubMed
-
- MacKenzie CR, Heseler K, Muller A, et al. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in antimicrobial defence and immuno-regulation: tryptophan depletion versus production of toxic kynurenines. Curr Drug Metab. 2007;8:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Fallarino F, Gizzi S, Mosci P, et al. Tryptophan catabolism in IDO+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Curr Drug Metab. 2007;8:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Mellor AL, Munn D, Chandler P, et al. Tryptophan catabolism and T cell responses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;527:27–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

