Cycle inhibiting factors (CIFs) are a growing family of functional cyclomodulins present in invertebrate and mammal bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 19308257
- PMCID: PMC2654923
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004855
Cycle inhibiting factors (CIFs) are a growing family of functional cyclomodulins present in invertebrate and mammal bacterial pathogens
Abstract
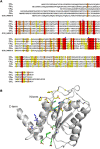
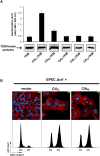
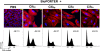
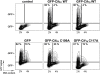
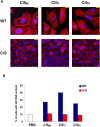
The cycle inhibiting factor (Cif) produced by enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli was the first cyclomodulin to be identified that is injected into host cells via the type III secretion machinery. Cif provokes cytopathic effects characterized by G(1) and G(2) cell cycle arrests, accumulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) p21(waf1/cip1) and p27(kip1) and formation of actin stress fibres. The X-ray crystal structure of Cif revealed it to be a divergent member of a superfamily of enzymes including cysteine proteases and acetyltransferases that share a conserved catalytic triad. Here we report the discovery and characterization of four Cif homologs encoded by different pathogenic or symbiotic bacteria isolated from vertebrates or invertebrates. Cif homologs from the enterobacteria Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, Photorhabdus luminescens, Photorhabdus asymbiotica and the beta-proteobacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei all induce cytopathic effects identical to those observed with Cif from pathogenic E. coli. Although these Cif homologs are remarkably divergent in primary sequence, the catalytic triad is strictly conserved and was shown to be crucial for cell cycle arrest, cytoskeleton reorganization and CKIs accumulation. These results reveal that Cif proteins form a growing family of cyclomodulins in bacteria that interact with very distinct hosts including insects, nematodes and humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cycle inhibiting factors (cifs): cyclomodulins that usurp the ubiquitin-dependent degradation pathway of host cells.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Apr;3(4):356-68. doi: 10.3390/toxins3040356. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cif type III effector protein: a smart hijacker of the host cell cycle.Future Microbiol. 2009 Sep;4(7):867-77. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.60. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19722840 Review.
-
Bacterial cyclomodulin Cif blocks the host cell cycle by stabilizing the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Dec;10(12):2496-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01224.x. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18705694
-
Crystal structures of Cif from bacterial pathogens Photorhabdus luminescens and Burkholderia pseudomallei.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005582. Epub 2009 May 18. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19440549 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the cyclomodulin Cif from pathogenic Escherichia coli.J Mol Biol. 2008 Dec 12;384(2):465-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.051. Epub 2008 Sep 27. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18845161 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cycle inhibiting factors (cifs): cyclomodulins that usurp the ubiquitin-dependent degradation pathway of host cells.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Apr;3(4):356-68. doi: 10.3390/toxins3040356. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melioidosis: molecular aspects of pathogenesis.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014 Dec;12(12):1487-99. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.970634. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014. PMID: 25312349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous Family of Cyclomodulins: Smart Weapons That Allow Bacteria to Hijack the Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Promote Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 23;7:208. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00208. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28589102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic reprogramming of host cells by bacterial pathogens.F1000 Biol Rep. 2009 Oct 29;1:80. doi: 10.3410/B1-80. F1000 Biol Rep. 2009. PMID: 20948607 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-related processes and innate immunity in C. elegans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4305-4333. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03787-w. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33630111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oswald E, Nougayrede JP, Taieb F, Sugai M. Bacterial toxins that modulate host cell-cycle progression. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Nougayrede JP, Taieb F, De Rycke J, Oswald E. Cyclomodulins: bacterial effectors that modulate the eukaryotic cell cycle. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Marches O, Ledger TN, Boury M, Ohara M, Tu X, et al. Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli deliver a novel effector called Cif, which blocks cell cycle G2/M transition. Mol Microbiol. 2003;50:1553–1567. - PubMed
-
- Taieb F, Nougayrede JP, Watrin C, Samba-Louaka A, Oswald E. Escherichia coli cyclomodulin Cif induces G2 arrest of the host cell cycle without activation of the DNA-damage checkpoint-signalling pathway. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:1910–1921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

