Talonavicular joint arthrodesis for the treatment of pes planus valgus in older children and adolescents with cerebral palsy
- PMID: 19308477
- PMCID: PMC2686809
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-009-0168-7
Talonavicular joint arthrodesis for the treatment of pes planus valgus in older children and adolescents with cerebral palsy
Abstract
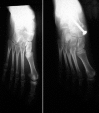
Purpose: The purpose of this report is to review our experience with talonavicular joint arthrodesis for the treatment of severe valgus foot deformities in older children and adolescents with cerebral palsy (CP).
Methods: The clinical, radiographic, and gait parameters results after talonavicular joint arthrodesis were retrospectively reviewed in 32 patients (59 feet) with valgus deformities of the foot. The surgery was performed as part of multiple simultaneous surgeries for the treatment of gait disorders. The mean age of the patients was 13.9 years (range 9-20 years) and the mean follow-up was 40 months (range 18.3-66.7 months).
Results: The clinical and radiographic measurements improved significantly (P = 0.000). There were no significant changes in gait parameters. Symptoms were relieved in most patients with symptomatic preoperative feet. The most frequent complication was pseudoarthrosis, which occurred in seven feet. We found a high rate of satisfaction of patients (or parents) and most of them recommended the procedure to other patients with the same condition.
Conclusion: Talonavicular joint arthrodesis is a reliable technique that provides both functionally and cosmetically good results with a low rate of complications in the treatment of severe pes planus valgus in older children and adolescents with CP. Careful examination should rule out concomitant ankle valgus deformities. A stable fixation of the arthrodesis is recommended.
Figures



References
-
- Gage JR. Gait analysis in cerebral palsy. London: Mac Keith Press; 1991. p. 157.
-
- Gage JR, Schwartz ML. Pathological gait and lever-arm dysfunction. In: Gage JR, editor. The treatment of gait problems in cerebral palsy. London: Mac Keith Press; 2004. p. 197.
-
- Herring JA. Disorders of the brain—cerebral palsy. In: Herring JA, editor. Tachdjian’s pediatric orthopaedics. 3. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2002. p. 1150.
-
- Dennyson WG, Fulford GE. Subtalar arthrodesis by cancellous grafts and metallic internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976;58:507–510. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

