Classification of proximal tibial fractures in children
- PMID: 19308478
- PMCID: PMC2686808
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-009-0167-8
Classification of proximal tibial fractures in children
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a classification system for all proximal tibial fractures in children that accounts for force of injury and fracture patterns.
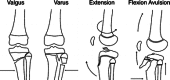
Methods: At our institution, 135 pediatric proximal tibia fractures were treated from 1997 to 2005. Fractures were classified into four groups according to the direction of force of injury: valgus, varus, extension, and flexion-avulsion. Each group was subdivided into metaphyseal and physeal type by fracture location and Salter-Harris classification. Also included were tibial tuberosity and tibial spine fractures.
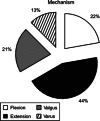
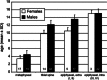
Results: Of the 135 fractures, 30 (22.2%) were classified as flexion group, 60 (44.4%) extension group, 28 (20.8%) valgus group, and 17 (12.6%) varus group. The most common type was extension-epiphyseal-intra-articular-tibial spine in 52 fractures (38.5%). This study shows that proximal tibial fractures are age-dependent in relation to: mechanism, location, and Salter-Harris type. In prepubescent children (ages 4-9 years), varus and valgus forces were the predominate mechanism of fracture creation. During the years nearing adolescence (around ages 10-12 years), a fracture mechanism involving extension forces predominated. With pubescence (after age 13 years), the flexion-avulsion pattern is most commonly seen. Furthermore, metaphyseal fractures predominated in the youngest population (ages 3-6 years), with tibial spine fractures occurring at age 10, Salter-Harris type I and II fractures at age 12, and Salter-Harris type III and IV physeal injuries occurring around age 14 years.
Conclusion: We propose a new classification scheme that reflects both the direction of force and fracture pattern that appears to be age-dependent. A better understanding of injury patterns based on the age of the child, in conjunction with appropriate pre-operative imaging studies, such as computer-aided tomography, will facilitate the operative treatment of these often complex fractures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative Analysis of Mechanism-Associated 3-Dimensional Tibial Plateau Fracture Patterns.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Mar 4;102(5):410-418. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.00485. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 31855868
-
Posterior tibial slope angle is associated with flexion-type Salter-Harris II and Watson-Jones type IV fractures of the proximal tibia.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019 Sep;27(9):2994-3000. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5319-2. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019. PMID: 30535547
-
Surgical management of a Salter-Harris type I proximal physeal fracture of the tibia in a foal: a case report.BMC Vet Res. 2022 May 16;18(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03285-6. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35578200 Free PMC article.
-
[Proximal tibial epiphyseal separation in adolescents. Apropos of 13 cases with 10 reviewed after 5 years].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1994;80(5):428-35. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1994. PMID: 7746928 French.
-
[Short-term effectiveness of ultrasound-guided Kirschner wire provocation technique in treatment of Salter-Harris types Ⅰ and Ⅱ periosteal entrapment of distal tibial epiphyseal fractures in children and adolescents].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 15;37(12):1477-1481. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202309047. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38130190 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Clinical and epidemiological features of tibial tubercle avulsion fracture in Chinese adolescents.World J Pediatr Surg. 2020 Sep 16;3(3):e000169. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2020-000169. eCollection 2020. World J Pediatr Surg. 2020. PMID: 36475273 Free PMC article.
-
Partial Remodeling after Conservative Treatment of Trampoline Fractures in Children.Children (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;10(2):282. doi: 10.3390/children10020282. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832411 Free PMC article.
-
Incarceration of the intermeniscal ligament in tibial eminence injury: a block to closed reduction identified using MRI.Skeletal Radiol. 2015 May;44(5):717-21. doi: 10.1007/s00256-014-2014-3. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Skeletal Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25283983
-
Proximal Tibial Epiphysis Fracture in a 13-Year-Old Male Athlete.Case Rep Orthop. 2017;2017:4823589. doi: 10.1155/2017/4823589. Epub 2017 May 21. Case Rep Orthop. 2017. PMID: 28607786 Free PMC article.
-
Tibial tubercle avulsion fracture during sport activities in adolescent: a case report.Acta Biomed. 2022 Mar 10;92(S3):e2021571. doi: 10.23750/abm.v92iS3.12580. Acta Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35604251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shelton WR, Canale ST. Fractures of the tibia through the proximal tibial epiphyseal cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:167–173. - PubMed
-
- Ogden JA, Tross RB, Murphy MJ. Fractures of the tibial tuberosity in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62-A:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Balthazar DA, Pappas AM. Acquired valgus deformity of the tibia in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984;4:538–541. - PubMed
-
- Jackson DW, Cozen L. Genu valgum as a complication of proximal tibial metaphyseal fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53:1571–1578. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

