Femoral shaft fractures treated with stainless steel flexible nails in children aged between 5 and 12 years at the HUSVP: a two-year follow-up
- PMID: 19308624
- PMCID: PMC2656945
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-008-0154-5
Femoral shaft fractures treated with stainless steel flexible nails in children aged between 5 and 12 years at the HUSVP: a two-year follow-up
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to show our experience with stainless steel flexible nails in the treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children aged between 5 and 12 years and to observe if the type of material used for nails affects the results.
Materials: A prospective, descriptive study of a series of cases was performed to evaluate patients treated at the Hospital Universitario San Vicente de Paúl (HUSVP) who had been followed up for at least 24 months.
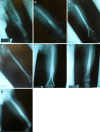
Results: The study group was composed of 48 patients, with an average age of 8.6 years. According to the AO classification, the most common type of fracture was 32A3.2 (61%). The average follow-up period was 43 months. The alterations observed were six cases of clinical length discrepancy, two cases of overgrowing, four cases of shortening, and two malunions in valgus. These alterations had no repercussion in the children's function. The follow-up is the main strength of this study, as it demonstrated that, 2 years after surgery.
Conclusion: The results with stainless steel nails are as good as those with titanium nails with a shorter follow-up as reported in the literature. Given the high costs of osteosynthesis material in our country, the results of this study provide a less expensive alternative. Level of evidence IV, case series.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures by stainless steel and titanium elastic nail system: A randomized comparative trial.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Aug 1;19(4):213-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.02.001. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 27578377 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) in paediatric femur and tibia shaft fractures: Comparison between titanium and stainless steel nails.Injury. 2018 Nov;49 Suppl 3:S8-S11. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.09.049. Injury. 2018. PMID: 30415674
-
Complications of titanium and stainless steel elastic nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Jun;90(6):1305-13. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.00328. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. PMID: 18519325
-
Flexible Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fractures in Children Weighing ≥40 kg: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Pediatr Orthop. 2020 Nov/Dec;40(10):562-568. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001574. J Pediatr Orthop. 2020. PMID: 33045158
-
Treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures with elastic stable intramedullary nails versus external fixation: A meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Nov;106(7):1305-1311. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.06.012. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33082120
Cited by
-
Rust score-An adequate rehabilitation guide for diaphyseal femur fractures managed by TENS.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019 Sep-Oct;10(5):922-927. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.06.010. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019. PMID: 31528069 Free PMC article.
-
An observational cohort study of the adoption of elastic stable intramedullary nailing for the treatment of pediatric femur fractures in Kumasi, Ghana.World J Surg. 2014 Nov;38(11):2818-24. doi: 10.1007/s00268-014-2664-2. World J Surg. 2014. PMID: 24964754
-
Treatment of pediatric femoral shaft fractures by stainless steel and titanium elastic nail system: A randomized comparative trial.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Aug 1;19(4):213-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.02.001. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 27578377 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hinton R, Lincoln A, Crockett M. Fractures of the femoral shaft in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(4):500–509. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JM, Schwend RM. Management of pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12(5):347–359. - PubMed
-
- Slongo TF, Zachariou Z. Treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children. AO Dialogue. 2005;2:15–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

