Characterization of peptidoglycan in fem-deletion mutants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by solid-state NMR
- PMID: 19309106
- PMCID: PMC2785074
- DOI: 10.1021/bi801750u
Characterization of peptidoglycan in fem-deletion mutants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by solid-state NMR
Abstract
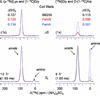
Compositional analysis of the peptidoglycan (PG) of a wild-type methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and its fem-deletion mutants has been performed on whole cells and cell walls using stable-isotope labeling and rotational-echo double-resonance NMR. The labels included [1-(13)C,(15)N]glycine and l-[epsilon-(15)N]lysine (for a direct measure of the number of glycyl residues in the bridging segment), [1-(13)C]glycine and l-[epsilon-(15)N]lysine (concentration of bridge links), and d-[1-(13)C]alanine and [(15)N]glycine (concentrations of cross-links and wall teichoic acids). The bridging segment length changed from 5.0 glycyl residues (wild-type strain) to 2.5 +/- 0.1 (FemB) with modest changes in cross-link and bridge-link concentrations. This accurate in situ measurement for the FemB mutant indicates a heterogeneous PG structure with 25% monoglycyl and 75% triglycyl bridges. When the bridging segment was reduced to a single glycyl residue 1.0 +/- 0.1 (FemA), the level of cross-linking decreased by more than 20%, resulting in a high concentration of open N-terminal glycyl segments.
Figures


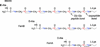
References
-
- Hiramatsu K, Cui L, Kuroda M, Ito T. The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:486–493. - PubMed
-
- Labischinski H. Consequences of the interaction of β-lactam antibiotics with penicillin-binding proteins from sensitive and resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992;181:241–265. - PubMed
-
- Berger-Bächi B, Tschierske M. Role of Fem factors in methicillin resistance. Drug Resist. Updates. 1998;1:325–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

