Conantokin-Br from Conus brettinghami and selectivity determinants for the NR2D subunit of the NMDA receptor
- PMID: 19309162
- PMCID: PMC3955384
- DOI: 10.1021/bi802259a
Conantokin-Br from Conus brettinghami and selectivity determinants for the NR2D subunit of the NMDA receptor
Abstract
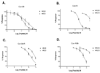
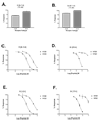
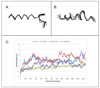
Conantokins are venom peptides from marine cone snails that are NMDA receptor antagonists. Here, we report the characterization of a 24 AA conantokin from Conus brettinghami Coomans , H. E. , Moolenbeek , R. G. and Wils , E. ( 1982 ) Basteria 46 ( 1/4 ), 3 - 67 , conantokin-Br (con-Br), the first conantokin that does not have the conserved glutamate residue at position 2. Molecular modeling studies suggest that con-Br has a helical structure between residues 2-13. In contrast to other characterized conantokins, con-Br has a high potency for NMDA receptors with NR2D subunits. To identify determinants for NR2D potency, we synthesized chimeras of con-Br and conantokin-R (con-R); the latter has a approximately 30-fold lower potency for the NR2D subtype. The characterization of two reciprocal chimeras (con-Br/R and con-R/Br), comprising the first 9-10 N-terminal AAs of each conantokin followed by the corresponding C-terminal AAs of the other conantokin demonstrates that determinants for NR2D selectivity are at the N-terminal region. Additional analogues comprising 1-3 amino acid substitutions from each peptide into the homologous region of the other led to the identification of a key determinant; a Tyr residue in position 5 increases potency for NR2D, while Val at this locus causes a decrease. The systematic definition of key determinants in the conantokin peptides for NMDA receptor subtype selectivity is an essential component in the development of conantokin peptides that are highly selective for each specific NMDA receptor subtype.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel conantokins from Conus parius venom are specific antagonists of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 21;282(51):36905-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706611200. Epub 2007 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17962189
-
From molecular phylogeny towards differentiating pharmacology for NMDA receptor subtypes.Toxicon. 2014 Apr;81:67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.01.016. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Toxicon. 2014. PMID: 24508768 Free PMC article.
-
Conantokin-P, an unusual conantokin with a long disulfide loop.Toxicon. 2008 Aug 1;52(2):203-13. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.04.178. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Toxicon. 2008. PMID: 18586049 Free PMC article.
-
Conantokins: peptide antagonists of NMDA receptors.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Dec;11(23):3073-84. doi: 10.2174/0929867043363901. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15579001 Review.
-
Structure-function relationships of the NMDA receptor antagonist conantokin peptides.Curr Drug Targets. 2001 Sep;2(3):313-22. doi: 10.2174/1389450013348542. Curr Drug Targets. 2001. PMID: 11554555 Review.
Cited by
-
Conotoxin gene superfamilies.Mar Drugs. 2014 Dec 17;12(12):6058-101. doi: 10.3390/md12126058. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25522317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the Conus bullatus genome and its venom-duct transcriptome.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jan 25;12:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-60. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21266071 Free PMC article.
-
Conantokins derived from the Asprella clade impart conRl-B, an N-methyl d-aspartate receptor antagonist with a unique selectivity profile for NR2B subunits.Biochemistry. 2012 Jun 12;51(23):4685-92. doi: 10.1021/bi300055n. Epub 2012 May 30. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22594498 Free PMC article.
-
Metal ion determinants of conantokin dimerization as revealed in the X-ray crystallographic structure of the Cd(2+)/Mg (2+)-con-T[K7gamma] complex.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010 Jun;15(5):667-75. doi: 10.1007/s00775-010-0633-2. Epub 2010 Mar 2. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010. PMID: 20195692 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic messiness in the venom duct of Conus miles contributes to conotoxin diversity.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Dec;12(12):3824-33. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.030353. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 24043424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coomans HE, Moolenbeek RG, Wils E. Alphabetical revision of the (sub)species in recent Conidae 5. baccatus to byssinus, including Conus brettinghami nomen novum . Basteria. 1982;46(1/4):3–67.
-
- Simeone TA, Sanchez RM, Rho JM. Molecular biology and ontogeny of glutamate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. J Child Neurol. 2004;19:343–360. discussion 361. - PubMed
-
- Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
-
- Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. Third Edition. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc; 2001.
-
- Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

