The impact of evidence-based practice implementation and fidelity monitoring on staff turnover: evidence for a protective effect
- PMID: 19309186
- PMCID: PMC2742697
- DOI: 10.1037/a0013223
The impact of evidence-based practice implementation and fidelity monitoring on staff turnover: evidence for a protective effect
Abstract
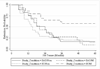
Staff retention is an ongoing challenge in mental health and community-based service organizations. Little is known about the impact of evidence-based practice implementation on the mental health and social service workforce. The present study examined the effect of evidence-based practice implementation and ongoing fidelity monitoring on staff retention in a children's services system. The study took place in the context of a statewide, regionally randomized effectiveness trial of an evidence-based intervention designed to reduce child neglect. In the study 21 teams consisting of 153 home-based service providers were followed over a 29-month period. Survival analyses revealed greater staff retention in the condition where the evidence-based practice was implemented along with ongoing fidelity monitoring presented to staff as supportive consultation. These results should help to allay concerns about staff retention when implementing evidence-based practices where there is good values-innovation fit and when fidelity monitoring is designed as an aid and support to service providers in providing a high standard of care for children and families.
Figures
References
-
- Aarons GA, Palinkas LA. Implementation of evidence-based practice in child welfare: Service provider perspectives. Administration and Policy in Mental Health & Mental Health Services Research. 2007;34:411–419. - PubMed

