G protein-coupled receptor hetero-dimerization: contribution to pharmacology and function
- PMID: 19309353
- PMCID: PMC2795239
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00169.x
G protein-coupled receptor hetero-dimerization: contribution to pharmacology and function
Abstract
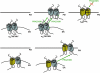
The concept that G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) can form hetero-dimers or hetero-oligomers continues to gain experimental support. However, with the exception of the GABA(B) receptor and the sweet and umami taste receptors few reported examples meet all of the criteria suggested in a recent International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology sponsored review (Pin et al., 2007) that should be required to define distinct and physiologically relevant receptor species. Despite this, there are many examples in which pairs of co-expressed GPCRs reciprocally modulate their function, trafficking and/or ligand pharmacology. Such data are at least consistent with physical interactions between the receptor pairs. In recent times, it has been suggested that specific GPCR hetero-dimer or hetero-oligomer pairs may represent key molecular targets of certain clinically effective, small molecule drugs and there is growing interest in efforts to identify ligands that may modulate hetero-dimer function selectively. The current review summarizes key recent developments in these topics.
Figures
References
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, el Massiery A, Quitterer U. Increased AT(1) receptor heterodimers in preeclampsia mediate enhanced angiotensin II responsiveness. Nat Med. 2001;7:1003–1009. - PubMed
-
- AbdAlla S, Abdel-Baset A, Lother H, El Massiery A, Quitterer U. Mesangial AT1/B2 receptor heterodimers contribute to angiotensin II hyperresponsiveness in experimental hypertension. J Mol Neurosci. 2005;26:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Bakker RA, Dees G, Carrillo JJ, Booth RG, López-Gimenez JF, Milligan G, et al. Domain swapping in the human histamine H1 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:131–318. - PubMed
-
- Banères JL, Parello J. Structure-based analysis of GPCR function: evidence for a novel pentameric assembly between the dimeric leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and the G-protein. J Mol Biol. 2003;329:815–829. - PubMed
-
- Barki-Harrington L, Luttrell LM, Rockman HA. Dual inhibition of beta-adrenergic and angiotensin II receptors by a single antagonist: a functional role for receptor-receptor interaction in vivo. Circulation. 2003;108:1611–1618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G9811527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/D001951/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 076774/Z/05/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/E006302/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

