Duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytes of children with cow milk allergy preferentially bind the glycan-binding protein galectin-3
- PMID: 19309568
- PMCID: PMC3844523
- DOI: 10.1177/039463200902200123
Duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytes of children with cow milk allergy preferentially bind the glycan-binding protein galectin-3
Abstract
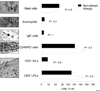
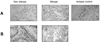
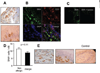
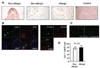
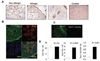
A breakdown in intestinal homeostasis results in inflammatory bowel diseases including coeliac disease and allergy. Galectins, evolutionarily conserved beta-galactoside-binding proteins, can modulate immune-epithelial cell interactions by influencing immune cell fate and cytokine secretion. In this study we investigated the glycosylation signature, as well as the regulated expression of galectin-1 and -3 in human duodenal samples of allergic and non-allergic children. Whereas galectin-1 was predominantly localized in the epithelial compartment (epithelial cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes) and the underlying lamina propria (T cells, macrophages and plasma cells), galectin-3 was mainly expressed by crypt epithelial cells and macrophages in the lamina propria. Remarkably, expression of these galectins was not significantly altered in allergic versus non-allergic patients. Investigation of the glycophenotype of the duodenal inflammatory microenvironment revealed substantial alpha2-6-linked sialic acid bound to galactose in lamina propria plasma cells, macrophages and intraepithelial lymphocytes and significant levels of asialo core 1 O-glycans in CD68+ macrophages and enterocytes. Galectin-1 preferentially bound to neutrophils, plasma cells and enterocytes, while galectin-3 binding sites were mainly distributed on macrophages and intraepithelial lymphocytes. Notably, galectin-3, but not galectin-1 binding, was substantially increased in intraepithelial gut lymphocytes of allergic patients compared to non-allergic subjects, suggesting a potential role of galectin-3-glycan interactions in shaping epithelial-immune cell connections during allergic inflammatory processes.
Figures

References
-
- Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:S470–S475. - PubMed
-
- Romagnani S. The role of lymphocytes in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Frydas S, Karagouni E, Hatzistilianou M, et al. Cytokines and allergic disorders: revisited study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004;17:233–235. - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Karttunen TJ, Kokkonen J. TIA1 and mast cell tryptase in food allergy of children: increase of intraepithelial lymphocytes expressing TIA1 associates with allergy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001;32:11–18. - PubMed
-
- van Kooyk Y, Rabinovich GA. Protein-glycan interactions in the control of innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:593–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

