Prenatal ethanol exposure persistently impairs NMDA receptor-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the mouse dentate gyrus
- PMID: 19317851
- PMCID: PMC2693081
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06049.x
Prenatal ethanol exposure persistently impairs NMDA receptor-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the mouse dentate gyrus
Abstract
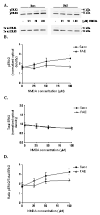
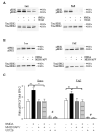
The dentate gyrus (DG) is the central input region to the hippocampus and is known to play an important role in learning and memory. Previous studies have shown that prenatal alcohol is associated with hippocampal-dependent learning deficits and a decreased ability to elicit long-term potentiation (LTP) in the DG in adult animals. Given that activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling cascade by NMDA receptors is required for various forms of learning and memory, as well as LTP, in hippocampal regions, including the DG, we hypothesized that fetal alcohol-exposed adult animals would have deficits in hippocampal NMDA receptor-dependent ERK1/2 activation. We used immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry techniques to detect NMDA-stimulated ERK1/2 activation in acute hippocampal slices prepared from adult fetal alcohol-exposed mice. We present the first evidence linking prenatal alcohol exposure to deficits in NMDA receptor-dependent ERK1/2 activation specifically in the DG of adult offspring. This deficit may account for the LTP deficits previously observed in the DG, as well as the life-long cognitive deficits, associated with prenatal alcohol exposure.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Moderate prenatal alcohol exposure reduces plasticity and alters NMDA receptor subunit composition in the dentate gyrus.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):1062-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1217-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325244 Free PMC article.
-
Selective vulnerability of hippocampal cornu ammonis 1 pyramidal cells to excitotoxic insult is associated with the expression of polyamine-sensitive N-methyl-D-asparate-type glutamate receptors.Neuroscience. 2010 Jan 20;165(2):525-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.018. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19837138 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental lead (Pb) exposure reduces the ability of the NMDA antagonist MK-801 to suppress long-term potentiation (LTP) in the rat dentate gyrus, in vivo.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007 May-Jun;29(3):385-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2007.01.006. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007. PMID: 17350801
-
Prenatal ethanol exposure reduces mGluR5 receptor number and function in the dentate gyrus of adult offspring.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004 Oct;28(10):1587-97. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000141815.21602.82. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004. PMID: 15597093
-
Sex-specific deficits in biochemical but not behavioral responses to delay fear conditioning in prenatal alcohol exposure mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Dec;156:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 30316893 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of the histamine H(3) receptor agonist methimepip on dentate granule cell excitability, paired-pulse plasticity and long-term potentiation in prenatal alcohol-exposed rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Jul;38(7):1902-11. doi: 10.1111/acer.12430. Epub 2014 May 12. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24818819 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of moderate prenatal ethanol exposure on the differential expression of two histamine H3 receptor isoforms in different brain regions of adult rat offspring.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;17:1192096. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1192096. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37449267 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Cxcl12a/Cxcr4b Chemokine System in Mediating the Stimulatory Effect of Embryonic Ethanol Exposure on Neuronal Density in Zebrafish Hypothalamus.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Dec;44(12):2519-2535. doi: 10.1111/acer.14482. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 33067812 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates behavioral alterations associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in rats.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2010 Oct;88(10):827-37. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20713. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 20706995 Free PMC article.
-
A limited access mouse model of prenatal alcohol exposure that produces long-lasting deficits in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Mar;36(3):457-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01644.x. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 21933200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan AM, Chynoweth J, Tyler LA, Caldwell KK. A mouse model of prenatal ethanol exposure using a voluntary drinking paradigm. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:2009–2016. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Banko JL, Hou L, Klann E. NMDA receptor activation results in PKA- and ERK- dependent Mnk1 activation and increased eIF4E phosphorylation in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurochem. 2004;91:462–470. - PubMed
-
- Berman RF, Hannigan JH. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the hippocampus: spatial behavior, electrophysiology and neuroanatomy. Hippocampus. 2000;10:94–110. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard BA, Riley EP, Hannigan JH. Deficits on a spatial navigation task following prenatal exposure to ethanol. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987;9:253–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

