Interleukin-1beta enhances nucleotide-induced and alpha-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing in rat primary cortical neurons via up-regulation of the P2Y(2) receptor
- PMID: 19317852
- PMCID: PMC2710802
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06048.x
Interleukin-1beta enhances nucleotide-induced and alpha-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing in rat primary cortical neurons via up-regulation of the P2Y(2) receptor
Abstract
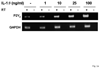
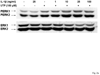
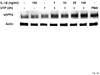
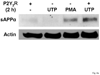
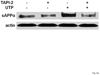
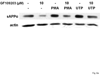
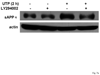
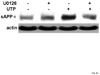
The heterologous expression and activation of the human P2Y(2) nucleotide receptor (P2Y(2)R) in human 1321N1 astrocytoma cells stimulates alpha-secretase-dependent cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), causing extracellular release of the non-amyloidogenic protein secreted amyloid precursor protein (sAPPalpha). To determine whether a similar response occurs in a neuronal cell, we analyzed whether P2Y(2)R-mediated production of sAPPalpha occurs in rat primary cortical neurons (rPCNs). In rPCNs, P2Y(2)R mRNA and receptor activity were virtually absent in quiescent cells, whereas overnight treatment with the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) up-regulated both P2Y(2)R mRNA expression and receptor activity by four-fold. The up-regulation of the P2Y(2)R was abrogated by pre-incubation with Bay 11-7085, an IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation inhibitor, which suggests that P2Y(2)R mRNA transcript levels are regulated through nuclear factor-kappa-B (NFkappaB) signaling. Furthermore, the P2Y(2)R agonist Uridine-5'-triphosphate (UTP) enhanced the release of sAPPalpha in rPCNs treated with IL-1beta or transfected with P2Y(2)R cDNA. UTP-induced release of sAPPalpha from rPCNs was completely inhibited by pre-treatment of the cells with the metalloproteinase inhibitor TACE inhibitor (TAPI-2) or the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002, and was partially inhibited by the MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor U0126 and the protein kinase C inhibitor GF109203. These data suggest that P2Y(2)R-mediated release of sAPPalpha from cortical neurons is directly dependent on a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) 10/17 and PI3K activity, whereas extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and PI3K activity may indirectly regulate APP processing. These results demonstrate that elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as IL-1beta, can enhance non-amyloidogenic APP processing through up-regulation of the P2Y(2)R in neurons.
Figures











Similar articles
-
P2Y2 nucleotide receptors enhance alpha-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 13;280(19):18696-702. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500219200. Epub 2005 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15778502
-
P2Y2 nucleotide receptor-mediated responses in brain cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;41(2-3):356-66. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8115-7. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20387013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptotanshinione upregulates alpha-secretase by activation PI3K pathway in cortical neurons.Brain Res. 2010 Aug 12;1348:165-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.083. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20595051
-
Interleukin-1alpha stimulates non-amyloidogenic pathway by alpha-secretase (ADAM-10 and ADAM-17) cleavage of APP in human astrocytic cells involving p38 MAP kinase.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Jul;84(1):106-18. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20864. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16724341
-
Role of the APP non-amyloidogenic signaling pathway and targeting alpha-secretase as an alternative drug target for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(27):2848-64. doi: 10.2174/092986707782360060. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 18045131 Review.
Cited by
-
P2 receptors for extracellular nucleotides in the central nervous system: role of P2X7 and P2Y₂ receptor interactions in neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Aug;46(1):96-113. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8263-z. Epub 2012 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22467178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supportive or detrimental roles of P2Y receptors in brain pathology?--The two faces of P2Y receptors in stroke and neurodegeneration detected in neural cell and in animal model studies.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Dec;11(4):441-54. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9471-6. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26407872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial purinergic signaling in Alzheimer's disease.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-10029-8. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38910192 Review.
-
Antagonistic Roles of P2X7 and P2Y2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 12;12:659097. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.659097. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33912064 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
P2Y receptors in the mammalian nervous system: pharmacology, ligands and therapeutic potential.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Sep;11(6):722-38. doi: 10.2174/187152712803581047. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22963441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn JS, Camden JM, Schrader AM, Redman RS, Turner JT. Reversible regulation of P2Y2 nucleotide receptor expression in the duct-ligated rat submandibular gland. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;279:C286–C294. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:734–744. Review. - PubMed
-
- Allinson TM, Parkin ET, Turner AJ, Hooper NM. ADAMs family members as amyloid precursor protein alpha-secretases. J Neurosci Res. 2003;74:342–352. - PubMed
-
- Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumor-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

