Genetics of the P2X7 receptor and human disease
- PMID: 19319666
- PMCID: PMC2686826
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-009-9136-4
Genetics of the P2X7 receptor and human disease
Abstract
The P2RX7 gene is highly polymorphic, and many single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) underlie the wide variation observed in P2X7 receptor responses. We review the discovery of those non-synonymous SNPs that affect receptor function and compare their frequencies in different ethnic populations. Analysis of pairwise linkage disequilibrium (LD) predicts a limited range of haplotypes. The strong LD between certain functional SNPs provides insight into published studies of the association between SNPs and human disease.
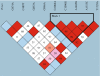
Figures

References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nature03001', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03001'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15496913', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15496913/'}]}
- International Human Genome Consortium (2004) Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 431(7011):931–45 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nature04226', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04226'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1880871', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1880871/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16255080', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16255080/'}]}
- The International HapMap Consortium (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437(7063):1299–1320 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1086/301749', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1086/301749'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1376944', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1376944/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9497246', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9497246/'}]}
- Ford D, Easton DF, Stratton M, Narod S, Goldgar D, Devilee P et al (1998) Genetic heterogeneity and penetrance analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in breast cancer families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 62(3):676–689 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/jmg.28.5.289', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.28.5.289'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1016845', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1016845/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1650842', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1650842/'}]}
- Burn J, Chapman P, Delhanty J, Wood C, Lalloo F, Cachon-Gonzalez MB et al (1991) The UK Northern region genetic register for familial adenomatous polyposis coli: use of age of onset, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, and DNA markers in risk calculations. J Med Genet 28(5):289–296 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nature05911', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05911'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2719288', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2719288/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17554300', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17554300/'}]}
- The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (2007) Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447(7145):661–678 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

