Spinal astrogliosis in pain models: cause and effects
- PMID: 19319675
- PMCID: PMC11506094
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9390-6
Spinal astrogliosis in pain models: cause and effects
Abstract
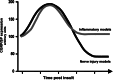
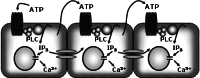
Pathological pain has been subjected to intense research to shed light on the underlying mechanisms of key symptoms, such as allodynia and hyperalgesia. The main focus has by and large concerned plasticity of spinal cord neurons and the primary afferent nerves relaying peripheral information to the spinal cord. Animal pain models display an increased presence of reactive astrocytes in the spinal cord, but in contrast to neurons, little is known about how they contribute to abnormal pain sensation. However, astrocytes are now beginning to receive greater attention, and as new information is emerging, it appears that astrocytes undertake critical roles in manifesting pathological pain. Through the secretion of diffusible transmitters, such as interleukins, ATP, and NO, astrocytes may augment primary afferent neuronal signaling or sensitize second order neurons in the spinal cord. In addition, astrocytes might lead to altered pain perception by a direct modulation of synaptic transmission between neurons in the nociceptive pathway or through the creation of astrocytic networks capable of transducing signals for extended distances across and along the spinal cord. Future research in astrocyte activation and signaling may therefore reveal novel drug targets for managing pathological pain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spinal microglia-derived TNF promotes the astrocytic JNK/CXCL1 pathway activation in a mouse model of burn pain.Brain Behav Immun. 2022 May;102:23-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Brain Behav Immun. 2022. PMID: 35143878
-
Inhibition of spinal astrocytic c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation correlates with the analgesic effects of ketamine in neuropathic pain.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Jan 24;8(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21255465 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal astrocytic c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation as counteracting mechanism to the amitriptyline analgesic efficacy in painful peripheral neuropathies.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 5;798:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.01.025. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28119076
-
Spinal astrocytes as therapeutic targets for pathological pain.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114(4):347-53. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10r04cp. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 21081837 Review.
-
Astrocytes--multitaskers in chronic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 15;716(1-3):120-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.03.023. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23528354 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Hyperalgesic Efficacy of Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALCAR) Against Visceral Pain Induced by Colitis: Involvement of Glia in the Enteric and Central Nervous System.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 2;24(19):14841. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914841. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834289 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple sclerosis-induced neuropathic pain: pharmacological management and pathophysiological insights from rodent EAE models.Inflammopharmacology. 2014 Feb;22(1):1-22. doi: 10.1007/s10787-013-0195-3. Inflammopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24234347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal astrocytes produce and secrete dynorphin neuropeptides.Neuropeptides. 2013 Apr;47(2):109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2012.10.006. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Neuropeptides. 2013. PMID: 23290538 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4-mediated autophagic impairment contributes to neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury mice.Mol Brain. 2018 Feb 27;11(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0354-y. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 29486776 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the beneficial effects of a GABA-based product containing Melissa officinalis on post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome: a preclinical study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1466824. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1466824. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39372212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed Z, Lewis CA, Faber DS (1990) Glutamate stimulates release of Ca2+ from internal stores in astroglia. Brain Res 516:165–169. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)90914-W - PubMed
-
- Anderson CM, Bergher JP, Swanson RA (2004) ATP-induced ATP release from astrocytes. J Neurochem 88:246–256 - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 22:208–215. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01349-6 - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG (2001) Dynamic signaling between astrocytes and neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 63:795–813. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.795 - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Wasner G (2001) Complex regional pain syndromes. Curr Pain Headache Rep 5:114–123. doi:10.1007/s11916-001-0079-x - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

