Fas-mediated apoptotic signaling in the mouse brain following reovirus infection
- PMID: 19321603
- PMCID: PMC2687381
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02488-08
Fas-mediated apoptotic signaling in the mouse brain following reovirus infection
Abstract
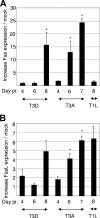
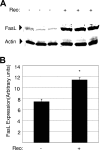
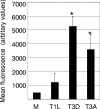
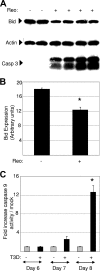
Type 3 (T3) reovirus strains induce apoptotic neuronal cell death and lethal encephalitis in infected mice. T3 strain Dearing (T3D)-induced apoptosis in primary neuronal cultures occurs by a Fas-mediated mechanism and requires the activation of caspase 8. We now show that Fas mRNA is upregulated in the brains of mice infected with encephalitic reovirus T3D and T3 strain Abney (T3A) but not following infection with nonencephalitic reovirus type 1 strain Lang. Fas is upregulated in regions of the brain that are injured during infection with T3 reovirus strains and colocalizes with virus antigen in individual neurons. In contrast, levels of FasL mRNA induced by encephalitic and nonencephalitic reovirus strains do not differ significantly. Caspase 8, the initiator caspase associated with Fas-mediated apoptosis, is activated in the cortex and hippocampal regions of both T3D- and T3A-infected mice. Furthermore, Bid cleavage and the activation of caspase 9 in the brains of T3D-infected mice suggest that the caspase 8-dependent activation of mitochondrial apoptotic signaling contributes to virus-induced apoptosis. We have previously shown that the inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling blocks T3D-induced apoptosis and improves the outcome of virus-induced encephalitis. We now show that the reovirus-induced upregulation of Fas requires JNK signaling, thereby providing a link between reovirus-induced death receptor signaling and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and a potential mechanism for the therapeutic action of JNK inhibition.
Figures


References
-
- Ashkenazi, A., and V. M. Dixit. 1998. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 2811305-1308. - PubMed
-
- Baloul, L., S. Camelo, and M. Lafon. 2004. Up-regulation of Fas ligand (FasL) in the central nervous system: a mechanism of immune evasion by rabies virus. J. Neurovirol. 10372-382. - PubMed
-
- Brozovic, S., R. Sahoo, S. Barve, H. Shiba, S. Uriarte, R. S. Blumberg, and D. F. Kinane. 2006. Porphyromonas gingivalis enhances FasL expression via up-regulation of NFkappaB-mediated gene transcription and induces apoptotic cell death in human gingival epithelial cells. Microbiology 152797-806. - PubMed
-
- Brunner, T., R. J. Mogil, D. LaFace, N. J. Yoo, A. Mahboubi, F. Echeverri, S. J. Martin, W. R. Force, D. H. Lynch, C. F. Ware, et al. 1995. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature 373441-444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

