Discovery of potent kisspeptin antagonists delineate physiological mechanisms of gonadotropin regulation
- PMID: 19321788
- PMCID: PMC3035813
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5740-08.2009
Discovery of potent kisspeptin antagonists delineate physiological mechanisms of gonadotropin regulation
Abstract
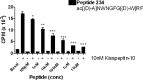
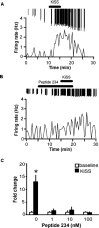
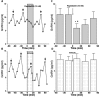
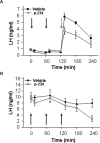
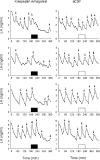
Neurons that produce gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) are the final common pathway by which the brain regulates reproduction. GnRH neurons are regulated by an afferent network of kisspeptin-producing neurons. Kisspeptin binds to its cognate receptor on GnRH neurons and stimulates their activity, which in turn provides an obligatory signal for GnRH secretion, thus gating down-stream events supporting reproduction. We have developed kisspeptin antagonists to facilitate the direct determination of the role of kisspeptin neurons in the neuroendocrine regulation of reproduction. In vitro and in vivo studies of analogues of kisspeptin-10 with amino substitutions have identified several potent and specific antagonists. A selected antagonist was shown to inhibit the firing of GnRH neurons in the brain of the mouse and to reduce pulsatile GnRH secretion in female pubertal monkeys; the later supporting a key role of kisspeptin in puberty onset. This analog also inhibited the kisspeptin-induced release of luteinizing hormone (LH) in rats and mice and blocked the postcastration rise in LH in sheep, rats, and mice, suggesting that kisspeptin neurons mediate the negative feedback effect of sex steroids on gonadotropin secretion in mammals. The development of kisspeptin antagonists provides a valuable tool for investigating the physiological and pathophysiological roles of kisspeptin in the regulation of reproduction and could offer a unique therapeutic agent for treating hormone-dependent disorders of reproduction, including precocious puberty, endometriosis, and metastatic prostate cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi S, Yamada S, Takatsu Y, Matsui H, Kinoshita M, Takase K, Sugiura H, Ohtaki T, Matsumoto H, Uenoyama Y, Tsukamura H, Inoue K, Maeda K. Involvement of anteroventral periventricular metastin/kisspeptin neurons in estrogen positive feedback action on luteinizing hormone release in female rats. J Reprod Dev. 2007;53:367–378. - PubMed
-
- Arai AC, Xia YF, Suzuki E, Kessler M, Civelli O, Nothacker HP. Cancer metastasis-suppressing peptide metastin upregulates excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal dentate granule cells. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:3648–3652. - PubMed
-
- Armeanu MC, Berkhout GM, Schoemaker J. Pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in hypothalamic amenorrhea, anorexia nervosa, and polycystic ovarian disease during naltrexone treatment. Fertil Steril. 1992;57:762–770. - PubMed
-
- Barker-Gibb ML, Scott CJ, Boublik JH, Clarke IJ. The role of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the control of LH secretion in the ewe with respect to season, NPY receptor subtype and the site of action in the hypothalamus. J Endocrinol. 1995;147:565–579. - PubMed
-
- Bilban M, Ghaffari-Tabrizi N, Hintermann E, Bauer S, Molzer S, Zoratti C, Malli R, Sharabi A, Hiden U, Graier W, Knöfler M, Andreae F, Wagner O, Quaranta V, Desoye G. Kisspeptin-10, a KiSS-1/metastin-derived decapeptide, is a physiological invasion inhibitor of primary human trophoblasts. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1319–1328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HD27142/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD027142/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 056157/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 HD015433/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD15433/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD11355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD011355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012629/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD056157/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD41469/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD041469/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD12629/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
