Involvement of erythropoietin in retinal ischemic preconditioning
- PMID: 19322943
- PMCID: PMC2891304
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819c4601
Involvement of erythropoietin in retinal ischemic preconditioning
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to examine the role of erythropoietin in retinal ischemic preconditioning (IPC).
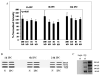
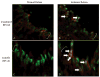
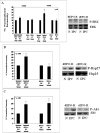
Methods: Rats were subjected to retinal ischemia after IPC. Electroretinography assessed functional recovery after ischemia; retinal sections were examined to determine loss of retinal ganglion cells, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling was used to assess apoptosis. Levels of downstream mediators were measured in retinal homogenates by Western blotting. To assess the involvement of erythropoietin in IPC, Western blotting was used to measure levels of erythropoietin and its receptor (EPO-R) in retinal homogenates after IPC. To examine erythropoietin's role in IPC, the impact of blocking erythropoietin via intravitreal injection of soluble EPO-R (sEPO-R) before IPC was studied.
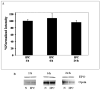
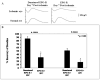
Results: Erythropoietin levels did not change after IPC, but EPO-R increased. Intravitreal injection of sEPO-R significantly attenuated both the functional and histologic neuroprotection produced by IPC in comparison to control injection of denatured sEPO-R. Apoptotic damage after ischemia was enhanced in the sEPO-R-treated retinas as indicated by fluorescent terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling. Phosphorylated extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and heat shock protein 27, but not protein kinase B, upregulated in denatured sEPO-R-treated retinae, were attenuated in eyes injected with sEPO-R.
Conclusions: These results indicate that EPO-R upregulation is a critical component of the functional, histologic, and antiapoptotic protective effect of IPC on ischemia in the retina and that several downstream effectors may be involved in the neuroprotective actions of erythropoietin.
Figures
References
-
- Roth S, Li B, Rosenbaum PS, Gupta H, Goldstein IM, Maxwell KM, Gidday JM. Preconditioning provides complete protection against retinal ischemic injury in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:775–85. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Roth S. Retinal ischemic preconditioning in the rat: requirement for adenosine and repetitive induction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40:1200–16. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Yang C, Rosenbaum DM, Roth S. Signal transduction mechanisms involved in ischemic preconditioning in the rat retina in vivo. Exp Eye Res. 2000;70:755–65. - PubMed
-
- Ettaiche M, Heurteaux C, Blondeau N, Borsotto M, Tinel N, Lazdunski M. ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) in retina: a key role for delayed ischemic tolerance. Brain Res. 2001;890:118–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

