Influence of intermittent hypoxia on myocardial and hepatic P-glycoprotein expression in a rodent model
- PMID: 19323616
- PMCID: PMC2873206
- DOI: 10.1592/phco.29.4.365
Influence of intermittent hypoxia on myocardial and hepatic P-glycoprotein expression in a rodent model
Abstract
Study objective: Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who receive drug therapy for cardiovascular disease may experience resistant hypertension, arrhythmias, or more severe heart failure, and many of the drugs used to treat these conditions are substrates for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporters. Therefore, we sought to determine if intermittent hypoxia, which mimics obstructive sleep apnea, would upregulate myocardial and hepatic P-gp expression and Abcb1a and Abcb1b messenger RNA (mRNA) expression (genes that encode for P-gp) in an animal model.
Design: Prospective, randomized, blinded, parallel-design animal study.
Setting: University research laboratory.
Animals: Thirty adult, male Sprague-Dawley rats.
Intervention: Rats were assigned to either 2 weeks of intermittent hypoxia exposure similar to sleep apnea (12 rats) or no hypoxia exposure (controls, 18 rats).
Measurements and main results: After intermittent hypoxia or normoxia exposure, the rats were anesthetized. Heart and liver were harvested, and small samples were taken from the left ventricle (heart) and the liver for analysis. Expression of P-gp was measured by Western blotting, whereas Abcb1a and Abcb1b mRNA expression was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Band density of myocardial (but not hepatic) P-gp expression (standardized by beta-actin) was significantly higher in hypoxic rats than in control rats (p=0.03). Quantitative polymerase chain reaction revealed that myocardial and hepatic Abcb1a and myocardial Abcb1b mRNA expression were significantly increased in hypoxic rats compared with controls (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Myocardial P-gp expression and myocardial and hepatic Abcb1a mRNA expression were significantly increased after 2 weeks of intermittent hypoxia. Hypoxia-induced increases in P-gp expression may partially explain drug-resistant cardiovascular disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: NONE DECLARED
Figures
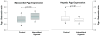


Similar articles
-
Short communication: Tissue-specific transcript expression of P-glycoprotein isoforms abcb1a and abcb1b in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following induction with clotrimazole.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Feb-Mar;252:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2020.110538. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33227421
-
Prandial state and biological sex modulate clinically relevant efflux transporters to different extents in Wistar and Sprague Dawley rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;160:114329. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114329. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36731343
-
Abcb1a and Abcb1b expression in senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM).Neurosci Lett. 2009 May 29;456(1):34-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.067. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19429129
-
Dexamethasone increases expression and activity of multidrug resistance transporters at the rat blood-brain barrier.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):C440-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00491.2007. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18524938 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Regulation Mechanisms of P-gp in the Blood-Brain Barrier in Hypoxia.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(10):1041-1051. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190610140153. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31187705 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the binding interactions between P-glycoprotein and eight known cardiovascular transport substrates.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015 Mar;3(2):e00114. doi: 10.1002/prp2.114. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25729581 Free PMC article.
-
In utero gene expression in the Slc39a8(neo/neo) knockdown mouse.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 16;8(1):10703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29109-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30013175 Free PMC article.
-
Altitude effect on Propofol Pharmacokinetics in Rats.Curr Drug Metab. 2024;25(1):81-90. doi: 10.2174/0113892002285571240220131547. Curr Drug Metab. 2024. PMID: 38468514 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal endotoxemia and placental drug transport in the mouse: placental size-specific effects.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 10;8(6):e65728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065728. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762418 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of P-Glycoprotein during Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;13(2):215. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020215. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Narkiewicz K, van de Borne PJ, Montano N, Dyken ME, Phillips BG, Somers VK. Contribution of tonic chemoreflex activation to sympathetic activity and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation. 1998;97(10):943–45. - PubMed
-
- Carpagnano GE, Kharitonov SA, Resta O, et al. 8-Isoprostane, a marker of oxidative stress, is increased in exhaled breath condensate of patients with obstructive sleep apnea after night and is reduced by continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Chest. 2003;124:1386–92. - PubMed
-
- Minoguchi K, Yokoe T, Tazaki T, et al. Increased carotid intima-media thickness and serum inflammatory markers in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:625–30. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Parker JD, Newton GE, et al. Influence of obstructive sleep apnea on mortality in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:1625–31. - PubMed
-
- Javaheri S, Parker TJ, Liming JD, et al. Sleep apnea in 81 ambulatory male patients with stable heart failure. Types and their prevalences, consequences, and presentations. Circulation. 1998;97:2154–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
