Discrete- and continuous-time probabilistic models and algorithms for inferring neuronal UP and DOWN states
- PMID: 19323637
- PMCID: PMC2799196
- DOI: 10.1162/neco.2009.06-08-799
Discrete- and continuous-time probabilistic models and algorithms for inferring neuronal UP and DOWN states
Abstract
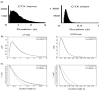
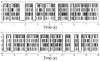
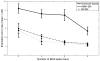
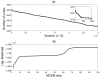
UP and DOWN states, the periodic fluctuations between increased and decreased spiking activity of a neuronal population, are a fundamental feature of cortical circuits. Understanding UP-DOWN state dynamics is important for understanding how these circuits represent and transmit information in the brain. To date, limited work has been done on characterizing the stochastic properties of UP-DOWN state dynamics. We present a set of Markov and semi-Markov discrete- and continuous-time probability models for estimating UP and DOWN states from multiunit neural spiking activity. We model multiunit neural spiking activity as a stochastic point process, modulated by the hidden (UP and DOWN) states and the ensemble spiking history. We estimate jointly the hidden states and the model parameters by maximum likelihood using an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm and a Monte Carlo EM algorithm that uses reversible-jump Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling in the E-step. We apply our models and algorithms in the analysis of both simulated multiunit spiking activity and actual multi- unit spiking activity recorded from primary somatosensory cortex in a behaving rat during slow-wave sleep. Our approach provides a statistical characterization of UP-DOWN state dynamics that can serve as a basis for verifying and refining mechanistic descriptions of this process.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Neural dynamics as sampling: a model for stochastic computation in recurrent networks of spiking neurons.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002211. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 22096452 Free PMC article.
-
Ensembles of spiking neurons with noise support optimal probabilistic inference in a dynamically changing environment.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Oct 23;10(10):e1003859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003859. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25340749 Free PMC article.
-
Hidden Markov models for the stimulus-response relationships of multistate neural systems.Neural Comput. 2011 May;23(5):1071-132. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00118. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Neural Comput. 2011. PMID: 21299424
-
Multi-compartment neuron and population encoding powered spiking neural network for deep distributional reinforcement learning.Neural Netw. 2025 Feb;182:106898. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106898. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Neural Netw. 2025. PMID: 39571385 Review.
-
Space-Time Dynamics of Membrane Currents Evolve to Shape Excitation, Spiking, and Inhibition in the Cortex at Small and Large Scales.Neuron. 2017 Jun 7;94(5):934-942. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.04.038. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28595049 Review.
Cited by
-
Explicit-duration hidden Markov model inference of UP-DOWN states from continuous signals.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021606. Epub 2011 Jun 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21738730 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional fibers enable modulation of cortical and deep brain activity during cognitive behavior in macaques.Sci Adv. 2023 Oct 6;9(40):eadh0974. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh0974. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37801492 Free PMC article.
-
Neural representation of spatial topology in the rodent hippocampus.Neural Comput. 2014 Jan;26(1):1-39. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00538. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Neural Comput. 2014. PMID: 24102128 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of bursts in extracellular spike trains using hidden semi-Markov point process models.J Comput Neurosci. 2010 Aug;29(1-2):203-212. doi: 10.1007/s10827-009-0182-2. Epub 2009 Aug 21. J Comput Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19697116
-
Network Model With Reduced Metabolic Rate Predicts Spatial Synchrony of Neuronal Activity.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 Oct 7;15:738362. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2021.738362. eCollection 2021. Front Comput Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34690730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achtman N, Afshar A, Santhanam G, Yu BM, Ryu SI, Shenoy KV. Free paced high-performance brain-computer interfaces. Journal of Neural Engineering. 2007;4:336–347. - PubMed
-
- Albert PS. A two-state Markov mixture model for a time series of epileptic seizure counts. Biometrics. 1991;47:1371–1381. - PubMed
-
- Ball FG, Cai Y, Kadane JB, O'Hagan A. Bayesian inference for ion-channel gating mechanisms directly from single-channel recordings, using Markov chain Monte Carlo. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, A. 1999;455:2879–2932.
-
- Bannerjee AK, Bhattacharyya GK. Bayesian results for the inverse gaussian distribution with an application. Technometrics. 1979;21(2):247–251.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

