JNets: exploring networks by integrating annotation
- PMID: 19323810
- PMCID: PMC2674432
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-95
JNets: exploring networks by integrating annotation
Abstract
Background: A common method for presenting and studying biological interaction networks is visualization. Software tools can enhance our ability to explore network visualizations and improve our understanding of biological systems, particularly when these tools offer analysis capabilities. However, most published network visualizations are static representations that do not support user interaction.
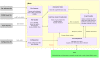
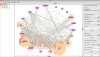
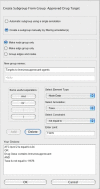
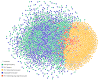
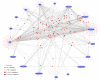
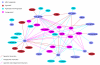
Results: JNets was designed as a network visualization tool that incorporates annotation to explore the underlying features of interaction networks. The software is available as an application and a configurable applet that can provide a flexible and dynamic online interface to many types of network data. As a case study, we use JNets to investigate approved drug targets present within the HIV-1 Human protein interaction network. Our software highlights the intricate influence that HIV-1 has on the host immune response.
Conclusion: JNets is a software tool that allows interaction networks to be visualized and studied remotely, from within a standard web page. Therefore, using this free software, network data can be presented in an enhanced, interactive format. More information about JNets is available at http://www.manchester.ac.uk/bioinformatics/jnets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BisoGenet: a new tool for gene network building, visualization and analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Feb 17;11:91. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-91. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20163717 Free PMC article.
-
VisANT: an online visualization and analysis tool for biological interaction data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Feb 19;5:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-17. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15028117 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated web visualizations for protein-protein interaction databases.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jun 16;16(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0615-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26077899 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics toolbox for exploring protein phosphorylation network.Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbaa134. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa134. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32666116 Review.
-
Biomolecule and Bioentity Interaction Databases in Systems Biology: A Comprehensive Review.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):1245. doi: 10.3390/biom11081245. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and dynamics of molecular networks: a novel paradigm of drug discovery: a comprehensive review.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun;138(3):333-408. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.016. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23384594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of HIV-1 protein interaction identify perturbed host-cellular subsystems.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Jul 29;6(7):e1000863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000863. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20686668 Free PMC article.
-
NAViGaTOR: Network Analysis, Visualization and Graphing Toronto.Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec 15;25(24):3327-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp595. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19837718 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1, human interaction database: current status and new features.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D566-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1126. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25378338 Free PMC article.
-
Network analyses in systems pharmacology.Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 1;25(19):2466-72. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp465. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19648136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

