The effect of sterilizing diseases on host abundance and distribution along environmental gradients
- PMID: 19324815
- PMCID: PMC2677222
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2008.1256
The effect of sterilizing diseases on host abundance and distribution along environmental gradients
Abstract
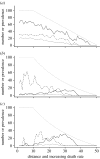
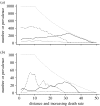
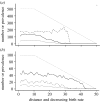
This study analyses the effect of host-specific pathogens on range restriction of their hosts across environmental gradients at population margins. Sterilizing diseases can limit host range by causing large reductions in population size in what would otherwise be the central area of a species range. Diseases showing frequency-dependent transmission can also pull back a population from its disease-free margin. A wide range of disease prevalence versus abundance patterns emerge which often differ from the classical expectation of increasing prevalence with increasing abundance. Surprisingly, very few empirical studies have investigated the dynamics of disease across environmental gradients or at range limits.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander H.M., Price S., Houser R., Finch D., Tourtellot M. Is there reduction in disease and predispersal seed predation at the border of a host plant's range? Field and herbarium studies of Carex blanda. J. Ecol. 2007;95:446–457. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2007.01228.x - DOI
-
- Alonso D., McKane A.J., Pascual M. Stochastic amplification in epidemics. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2007;4:575–582. doi:10.1098/rsif.2006.0192 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson R.M. Population dynamics of indirectly transmitted disease agents: the vector component. In: McKelvey J.J., Eldridge B.F., Maramorosch K., editors. Vectors of disease agents. Interactions with plants, animals, and man. Praeger; New York, NY: 1981. pp. 13–43.
-
- Anderson R.M., May R.M. The population dynamics of microparasites and their invertebrate hosts. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 1981;291:451–524. doi:10.1098/rstb.1981.0005 - DOI
-
- Antonovics J. The nature of limits to natural selection. Ann. Miss. Bot. Garden. 1976;63:224–247. doi:10.2307/2395303 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
