T cell receptor-mediated activation of p38{alpha} by mono-phosphorylation of the activation loop results in altered substrate specificity
- PMID: 19324872
- PMCID: PMC2708844
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M901004200
T cell receptor-mediated activation of p38{alpha} by mono-phosphorylation of the activation loop results in altered substrate specificity
Abstract
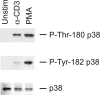
p38 MAPKs are typically activated by upstream MAPK kinases that phosphorylate a Thr-X-Tyr motif in the activation loop. An exception is the T cell antigen receptor signaling pathway, which bypasses the MAPK cascade and activates p38alpha and p38beta by phosphorylation of Tyr-323 and subsequent autophosphorylation of the activation loop. Here we show that, unlike the classic MAPK cascade, the alternative pathway results primarily in mono-phosphorylation of the activation loop residue Thr-180. Recombinant mono-phosphorylated and dual phosphorylated p38alpha differed widely with regard to activity and substrate preference. Altered substrate specificity was reproduced in T cells in which p38 was activated by the alternative or classical MAPK pathways. These findings suggest that T cells have evolved a mechanism to utilize p38 in a specialized manner independent of and distinct from the classical p38 MAPK signaling cascade.
Figures
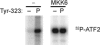




Similar articles
-
Enzymatic activity and substrate specificity of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38alpha in different phosphorylation states.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 26;283(39):26591-601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801703200. Epub 2008 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18669639 Free PMC article.
-
Activating p38 MAPK: new tricks for an old kinase.Cell Cycle. 2005 Sep;4(9):1189-92. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.9.2043. Epub 2005 Sep 20. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 16103752 Review.
-
p38alpha is active in vitro and in vivo when monophosphorylated at threonine 180.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 24;48(11):2497-504. doi: 10.1021/bi900024v. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19209848
-
Counter-regulation of T cell effector function by differentially activated p38.J Exp Med. 2014 Jun 2;211(6):1257-70. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131917. Epub 2014 May 26. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 24863062 Free PMC article.
-
The many paths to p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in the immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2006 Jul;6(7):532-40. doi: 10.1038/nri1865. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16799472 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective phosphorylation of the Dlg1AB variant is critical for TCR-induced p38 activation and induction of proinflammatory cytokines in CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2014 Sep 15;193(6):2651-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401196. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25098293 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal expression of MAPK14-related lncRNAs in the peripheral blood of patients with multiple sclerosis.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Apr 6;8(3):335-339. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.03.006. eCollection 2023 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37091283 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting treatment outcome using kinome activity profiling in HER2+ breast cancer biopsies.iScience. 2024 Apr 30;27(6):109858. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109858. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38784015 Free PMC article.
-
DEF pocket in p38α facilitates substrate selectivity and mediates autophosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19537-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.464511. Epub 2013 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23671282 Free PMC article.
-
c-Abl-p38α signaling pathway mediates dopamine neuron loss in trigeminal neuralgia.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920930855. doi: 10.1177/1744806920930855. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 32498644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J. ( 2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 807– 869 - PubMed
-
- Engelberg D. ( 2004) Semin. Cancer Biol. 14, 271– 282 - PubMed
-
- Lee J. C., Kumar S., Griswold D. E., Underwood D. C., Votta B. J., Adams J. L. ( 2000) Immunopharmacology 47, 185– 201 - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Jiang Y., Ulevitch R. J., Han J. ( 1996) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 228, 334– 340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

