Identification of loss of function mutations in human genes encoding RIG-I and MDA5: implications for resistance to type I diabetes
- PMID: 19324880
- PMCID: PMC2679434
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M809449200
Identification of loss of function mutations in human genes encoding RIG-I and MDA5: implications for resistance to type I diabetes
Abstract
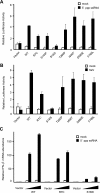
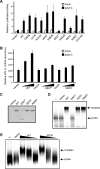
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) are essential for detecting viral RNA and triggering antiviral responses, including production of type I interferon. We analyzed the phenotype of non-synonymous mutants of human RIG-I and MDA5 reported in databases by functional complementation in cell cultures. Of seven missense mutations of RIG-I, S183I, which occurs within the second caspase recruitment domain repeat, inactivated this domain and conferred a dominant inhibitory function. Of 10 mutants of MDA5, two exhibited loss of function. A nonsense mutation, E627*, resulted in deletion of the C-terminal region and double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) binding activity. Another loss of function mutation, I923V, which occurs within the C-terminal domain, did not affect dsRNA binding activity, suggesting a novel and essential role for this residue in the signaling. Remarkably, these mutations are implicated in resistance to type I diabetes. However, the A946T mutation of MDA5, which has been implicated in type I diabetes by previous genetic analyses, affected neither dsRNA binding nor IFN gene activation. These results provide new insights into the structure-function relationship of RIG-I-like receptors as well as into human RIG-I-like receptor polymorphisms, antiviral innate immunity, and autoimmune diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Akira, S., Uematsu, S., and Takeuchi, O. (2006) Cell 124 783–801 - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama, M., Kikuchi, M., Natsukawa, T., Shinobu, N., Imaizumi, T., Miyagishi, M., Taira, K., Akira, S., and Fujita, T. (2004) Nat. Immun. 5 730–737 - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama, M., and Fujita, T. (2008) Immunity 29 178–181 - PubMed
-
- Cui, S., Eisenacher, K., Kirchhofer, A., Brzozka, K., Lammens, A., Lammens, K., Fujita, T., Conzelmann, K. K., Krug, A., and Hopfner, K. P. (2008) Mol. Cell 29 169–179 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

