The C-terminal half of human Ago2 binds to multiple GW-rich regions of GW182 and requires GW182 to mediate silencing
- PMID: 19324964
- PMCID: PMC2673069
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1229409
The C-terminal half of human Ago2 binds to multiple GW-rich regions of GW182 and requires GW182 to mediate silencing
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA)-mediated silencing is a post-transcriptional mechanism that regulates translation of mRNAs primarily via their 3'-UTR. Ago2 binds miRNA directly and is the core component of miRNA-induced silencing complex. GW182 is another important factor in miRNA-mediated silencing, and its interaction with Ago2 is evolutionarily conserved. However, the GW182-Ago2 interaction in humans has not been characterized thoroughly, and the role of GW182 in the mammalian miRNA pathway remains unclear. In the current study, we generated a set of GST-, green fluorescence protein (GFP)-, or 3xFlag-tagged deletion constructs of GW182 and Ago2 to further analyze GW182-Ago2 interactions. The C-terminal half of Ago2 interacted with four nonoverlapping GW-rich regions of GW182, and this interaction recruited Ago2 to GWB. Furthermore, the interaction with GW182 was observed in all four human Ago proteins. Most interestingly, tethering the C-terminal half of Ago2 to the 3'-UTR of reporter mRNA recapitulated translational repression comparable to that of tethered Ago2, and this repression was greatly impaired upon GW182 knockdown. In comparison, the N-terminal half of Ago2 did not bind GW182 and did not retain the repression function of Ago2. Our data strongly support a model in which Ago2 recruits GW182 to the 3'-UTR of mRNA to mediate silencing, and suggest that GW182 may contribute to enhancement in translational repression by interacting with multiple Ago proteins from multiple miRNA target sites in the same or adjacent 3'UTR.
Figures


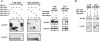

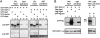


Similar articles
-
Mapping of Ago2-GW182 functional interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;725:45-62. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-046-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21528446
-
Mammalian GW182 contains multiple Argonaute-binding sites and functions in microRNA-mediated translational repression.RNA. 2009 Jun;15(6):1078-89. doi: 10.1261/rna.1363109. Epub 2009 Apr 27. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19398495 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of GW182 and its novel isoform TNGW1 as translational repressors in Ago2-mediated silencing.J Cell Sci. 2008 Dec 15;121(Pt 24):4134-44. doi: 10.1242/jcs.036905. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 19056672 Free PMC article.
-
Function of GW182 and GW bodies in siRNA and miRNA pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:71-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224966 Review.
-
The GW182 protein family in animal cells: new insights into domains required for miRNA-mediated gene silencing.RNA. 2009 Aug;15(8):1433-42. doi: 10.1261/rna.1703809. Epub 2009 Jun 17. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19535464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ethanol facilitates hepatitis C virus replication via up-regulation of GW182 and heat shock protein 90 in human hepatoma cells.Hepatology. 2013 Jan;57(1):70-80. doi: 10.1002/hep.26010. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 22898980 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 protein stabilizes unloaded argonaute complexes and microscopic P-bodies in human cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 May 1;21(9):1462-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-10-0885. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20237157 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs stimulate translation initiation mediated by HCV-like IRESes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 May 5;45(8):4810-4824. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1345. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28077561 Free PMC article.
-
From guide to target: molecular insights into eukaryotic RNA-interference machinery.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Jan;22(1):20-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2931. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25565029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus-specific miRNAs and Argonaute2 play a role in the viral life cycle.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047490. Epub 2012 Oct 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23091627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding L., Spencer A., Morita K., Han M. The developmental timing regulator AIN-1 interacts with miRISCs and may target the argonaute protein ALG-1 to cytoplasmic P bodies in C. elegans. Mol. Cell. 2005;19:437–447. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A., Huntzinger E., Izaurralde E. GW182 interaction with Argonaute is essential for miRNA-mediated translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008;15:346–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
