MicroRNA regulation of cardiovascular development
- PMID: 19325160
- PMCID: PMC2664538
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.192872
MicroRNA regulation of cardiovascular development
Abstract
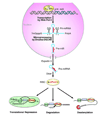
The transcriptional regulation of cardiovascular development requires precise spatiotemporal control of gene expression, and heterozygous mutations of transcription factors have frequently been implicated in human cardiovascular malformations. A novel mechanism involving posttranscriptional regulation by small, noncoding microRNAs (miRNAs) has emerged as a central regulator of many cardiogenic processes. We are beginning to understand the functions that miRNAs play during essential biological processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, stress response, and tumorigenesis. The identification of miRNAs expressed in specific cardiac and vascular cell types has led to the discovery of important regulatory roles for these small RNAs during cardiomyocyte differentiation, cell cycle, conduction, vessel formation, and during stages of cardiac hypertrophy in the adult. Here, we overview the recent findings on miRNA regulation in cardiovascular development and report the latest advances in understanding their function by unveiling their mRNA targets. Further analysis of miRNA function during cardiovascular development will allow us to determine the potential for novel miRNA-based therapeutic strategies.
Figures


References
-
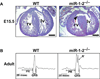
- Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, Vedantham V, von Drehle M, Muth AN, Tsuchihashi T, McManus MT, Schwartz RJ, Srivastava D. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell. 2007;129:303–317. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2002;39:1890–1900. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava D. Making or breaking the heart: from lineage determination to morphogenesis. Cell. 2006;126:1037–1048. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Srivastava D. A developmental view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:189–197. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

