The Rho-A/Rho-kinase pathway is up-regulated but remains inhibited by cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent mechanisms during endotoxemia in small mesenteric arteries
- PMID: 19325475
- PMCID: PMC2782480
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819efb43
The Rho-A/Rho-kinase pathway is up-regulated but remains inhibited by cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent mechanisms during endotoxemia in small mesenteric arteries
Abstract
Objective: We investigated whether a reduced activity in the Rho-A/Rho-kinase pathway could be involved in the impaired vascular reactivity observed in septic shock.
Design: Ex vivo animal study.
Setting: University research laboratory.
Subjects: Male Wistar rats.
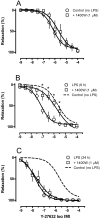
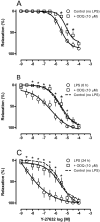
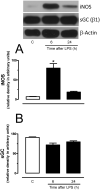
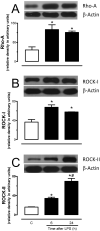
Interventions: Rats received an intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 mg/kg) either 6 or 24 hours before the onset of our experiments. The effects of Y-27632 (a Rho-kinase inhibitor) were assessed in first-order mesenteric rings taken from these animals using wire myograph. The expression of Rho-A, Rho-kinases I and II, and the total and phosphorylated myosin phosphatase targeting subunit 1 (MYPT1) were assessed by Western blotting.
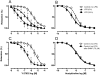
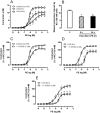
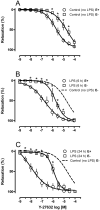
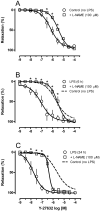
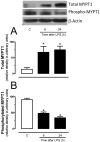
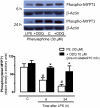
Measurements and main results: The EC50 to Y-27632 was reduced from 2.10 microM (1.22-3.66 microM) (control) to 0.21 microM (0.09-0.44 microM), and 9.54 (0.82-110.30) nM in LPS-treated groups 6 and 24 hours, respectively. The increased potency of Y-27632 was partially reversed by endothelium removal at both 6 and 24 hours. Incubation of Nomega-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride or 1400W (a nonselective and an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, respectively) normalized the responses to Y-27632 seen 6 hours after LPS. However, 1400W had no effect, whereas Nomega-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride caused a partial reduction in the enhanced potency of Y-27632 found 24 hours after LPS. The soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitor oxadiazolo[4,3-alpha]quinoxalin-1-one was able to bring the Y-27632 response back to normal both 6 and 24 hours after LPS. Rho-A, Rho-kinase I, Rho-kinase II, and MYPT1 were increased in mesenteric arteries from endotoxemic rats, but the phosphorylated MYPT1 was significantly reduced. However, incubation with oxadiazolo[4,3-alpha]quinoxalin-1-one circumvented the inhibition of MYPT1 phosphorylation found in preparations from LPS-treated animals.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed an impaired Rho-A/Rho-kinase-mediated phosphorylation of MYPT1 in vessels from endotoxemic animals in a cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent manner, suggesting that changes in mechanisms involved in calcium sensitization play a pivotal role in cardiovascular changes observed in septic shock.
Figures

Comment in
-
Vascular dysfunction in septic shock--any ROCKing news?Crit Care Med. 2009 May;37(5):1820-1. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a09408. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19373062 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Orthovanadate-Induced Vasoconstriction of Rat Mesenteric Arteries Is Mediated by Rho Kinase-Dependent Inhibition of Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(11):1809-16. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00587. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 26521832
-
Upregulation of Rho-kinase (ROCK-2) expression and enhanced contraction to endothelin-1 in the mesenteric artery from lipopolysaccharide-treated rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 13;498(1-3):211-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.092. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15363997
-
Increased activation of the Rho-A/Rho-kinase pathway in the renal vascular system is responsible for the enhanced reactivity to exogenous vasopressin in endotoxemic rats.Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun;42(6):e461-71. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000313. Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24690572
-
Induction of endothelium-dependent constriction of mesenteric arteries in endotoxemic hypotensive shock.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;173(7):1179-95. doi: 10.1111/bph.13415. Epub 2016 Mar 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26694894 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration by lipopolysaccharide of the relationship between intracellular calcium levels and contraction in rat mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(5):1218-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15526.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8818346 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Attenuated platelet aggregation in patients with septic shock is independent from the activity state of myosin light chain phosphorylation or a reduction in Rho kinase-dependent inhibition of myosin light chain phosphatase.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2015 Dec;3(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40635-014-0037-7. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2015. PMID: 26215804 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-Proteins and Downstream Pathways as Potential Targets in Sepsis and Septic Shock: What Have We Learned from Basic Research.Cells. 2021 Jul 21;10(8):1844. doi: 10.3390/cells10081844. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The suppression of myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation during the response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS): beneficial or detrimental to endothelial barrier?J Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;226(12):3132-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22669. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21302311 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin inhibits angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction on isolated mouse mesenteric resistance arteries through Rho-A- and PKA-dependent pathways.Vascul Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;58(4):313-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Vascul Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23268358 Free PMC article.
-
MLN4924, A Neddylation Inhibitor, Improves the Vascular Reactivity but Causes Early Mortality in Polymicrobial Sepsis: Effect on Vascular RhoA/ROCK Signaling.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Sep;25(9):1304-1320. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-10039-x. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40629201
References
-
- Mitolo-Chieppa D, Serio M, Potenza MA, et al. Hyporeactivity of mesenteric vascular bed in endotoxin-treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;309:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Trabold F, Sharshar T, et al. Inappropriate sympathetic activation at onset of septic shock: A spectral analysis approach. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:458–465. - PubMed
-
- Takakura K, Xiaohong W, Takeuchi K, et al. Deactivation of norepinephrine by peroxynitrite as a new pathogenesis in the hypotension of septic shock. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:928–934. - PubMed
-
- Takakura K, Taniguchi T, Muramatsu I, et al. Modification of alpha1-adrenoceptors by peroxynitrite as a possible mechanism of systemic hypotension in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:894–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

