A crosslinking analysis of GAP-43 interactions with other proteins in differentiated N1E-115 cells
- PMID: 19325830
- PMCID: PMC2635752
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms9091753
A crosslinking analysis of GAP-43 interactions with other proteins in differentiated N1E-115 cells
Abstract
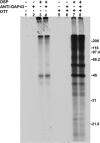
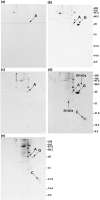
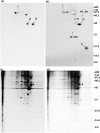
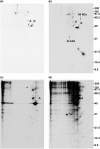
It has been suggested that GAP-43 (growth-associated protein) binds to various proteins in growing neurons as part of its mechanism of action. To test this hypothesis in vivo, differentiated N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells were labeled with [(35)S]-amino acids and were treated with a cleavable crosslinking reagent. The cells were lysed in detergent and the lysates were centrifuged at 100,000 x g to isolate crosslinked complexes. Following cleavage of the crosslinks and analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, it was found that the crosslinker increased the level of various proteins, and particularly actin, in this pellet fraction. However, GAP-43 was not present, suggesting that GAP-43 was not extensively crosslinked to proteins of the cytoskeleton and membrane skeleton and did not sediment with them. GAP-43 also did not sediment with the membrane skeleton following nonionic detergent lysis. Calmodulin, but not actin or other proposed interaction partners, co-immunoprecipitated with GAP-43 from the 100,000 x g supernatant following crosslinker addition to cells or cell lysates. Faint spots at 34 kDa and 60 kDa were also present. Additional GAP-43 was recovered from GAP-43 immunoprecipitation supernatants with anti-calmodulin but not with anti-actin. The results suggest that GAP-43 is not present in complexes with actin or other membrane skeletal or cytoskeletal proteins in these cells, but it is nevertheless possible that a small fraction of the total GAP-43 may interact with other proteins.
Keywords: CaM, calmodulin; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; DSP, dithiobis (succinimidyl propionate); DTT, dithiothreitol; GAP-43, growth-associated protein of 43 kDa; Neuromodulin; SDS, sodium dodecyl sulfate; cytoskeleton; filopodia; lipid rafts; palmitoylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chemical crosslinking of Plasmodium falciparum glycoprotein, Pf200 (190-205 kDa), to the S-antigen at the merozoite surface.Exp Parasitol. 1990 Feb;70(2):207-16. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90101-h. Exp Parasitol. 1990. PMID: 2404782
-
Dystrophin-related protein in the platelet membrane skeleton. Integrin-induced change in detergent-insolubility and cleavage by calpain in aggregating platelets.J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 10;270(45):27259-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.27259. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7592985
-
Association of solubilized angiotensin II receptors with phospholipase C-alpha in murine neuroblastoma NIE-115 cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;42(2):217-26. Mol Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1513321
-
Regulation of free calmodulin levels by neuromodulin: neuron growth and regeneration.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Mar;11(3):107-11. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90195-e. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990. PMID: 2151780 Review.
-
Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: impact on signaling and function: membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):532-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.018. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23899502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

