Cell stiffness, contractile stress and the role of extracellular matrix
- PMID: 19327344
- PMCID: PMC2956180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.118
Cell stiffness, contractile stress and the role of extracellular matrix
Abstract
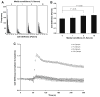
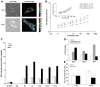
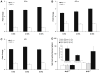
Here we have assessed the effects of extracellular matrix (ECM) composition and rigidity on mechanical properties of the human airway smooth muscle (ASM) cell. Cell stiffness and contractile stress showed appreciable changes from the most relaxed state to the most contracted state: we refer to the maximal range of these changes as the cell contractile scope. The contractile scope was least when the cell was adherent upon collagen V, followed by collagen IV, laminin, and collagen I, and greatest for fibronectin. Regardless of ECM composition, upon adherence to increasingly rigid substrates, the ASM cell positively regulated expression of antioxidant genes in the glutathione pathway and heme oxygenase, and disruption of a redox-sensitive transcription factor, nuclear erythroid 2 p45-related factor (Nrf2), culminated in greater contractile scope. These findings provide biophysical evidence that ECM differentially modulates muscle contractility and, for the first time, demonstrate a link between muscle contractility and Nrf2-directed responses.
Figures

References
-
- Bousquet J, Jeffery PK, Busse WW, Johnson M, Vignola AM. Asthma: from bronchoconstriction to airways inflammation and remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1720–1745. - PubMed
-
- Woolcock AJ, Peat JK. Epidemiology of bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1989;7:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JW, Li X. The measurement of reticular basement membrane and submucosal collagen in the asthmatic airway. Clin Expr Allergy. 1997;27:363–371. - PubMed
-
- Bosse Y, Pare PD, Seow CY. Airway wall remodeling in asthma: from the epithelial layer to the adventitia. Curr Allergy Asthma Reports. 2008;8:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Bai TR, Cooper J, Koelmeyer T, Pare PD, Weir TD. The effect of age and duration of disease on airway structure in fatal asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:663–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

