Role of eIF3a in regulating cell cycle progression
- PMID: 19327350
- PMCID: PMC11645673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.03.009
Role of eIF3a in regulating cell cycle progression
Abstract
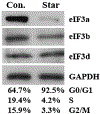
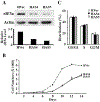
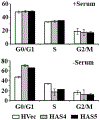
Translational control is an essential process in regulation of gene expression, which occurs at the initiation step performed by a number of translation initiation factor complexes. eIF3a (eIF3 p170) is the largest subunit of the eIF3 complex. eIF3a has been suggested to play roles in regulating translation of a subset of mRNAs and in regulating cell cycle progression and cell proliferation. In this study, we examined the expression profile of eIF3a in cell cycle and its role in cell cycle progression. We found that eIF3a expression oscillated with cell cycle and peaked in S phase. Reducing eIF3a expression also reduced cell proliferation rate by elongating cell cycle but did not change the cell cycle distribution. However, eIF3a appears to play an important role in cellular responses to external cell cycle modulators likely by affecting synthesis of target proteins of these modulators.
Figures
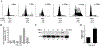



Similar articles
-
N-myc downstream regulated 1 (NDRG1) is regulated by eukaryotic initiation factor 3a (eIF3a) during cellular stress caused by iron depletion.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057273. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437357 Free PMC article.
-
The translational regulator eIF3a: the tricky eIF3 subunit!Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1806(2):275-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20647036 Review.
-
Aberration in translation initiation and associated diseases: Role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3A.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Oct 28;42(10):1204-1211. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2017.10.013. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 29093254
-
Role of eIF3 p170 in controlling synthesis of ribonucleotide reductase M2 and cell growth.Oncogene. 2004 May 6;23(21):3790-801. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207465. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15094776
-
eIF3a: A new anticancer drug target in the eIF family.Cancer Lett. 2018 Jan 1;412:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.055. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29031564 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between eIF3α polymorphism and severe toxicity caused by platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;75(2):516-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04379.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22804784 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Provides Evidence of Possible Axonal Overconnectivity in Frontal Lobes in Autism Spectrum Disorder Toddlers.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 15;79(8):676-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.06.029. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26300272 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-ethnic genome-wide association study implicates collagen matrix integrity and cell differentiation pathways in keratoconus.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 1;4(1):266. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01784-0. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33649486 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of eIF3a conditional knockout mice.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 19;10:1160063. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1160063. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37152897 Free PMC article.
-
RNA sequencing of MCF-7 breast cancer cells identifies novel estrogen-responsive genes with functional estrogen receptor-binding sites in the vicinity of their transcription start sites.Horm Cancer. 2013 Aug;4(4):222-32. doi: 10.1007/s12672-013-0140-3. Epub 2013 Mar 23. Horm Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23526455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hershey JWB, Merrick WC, Pathway and mechanism of initiation of protein synthesis, in: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB (Eds.), Translational Control of Gene Expression, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 2000, pp. 33–88.
-
- Dong Z, Zhang JT, Initiation factor eIF3 and regulation of mRNA translation, cell growth, and cancer, Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 59 (2006) 169–180. - PubMed
-
- Methot N, Rom E, Olsen H, Sonenberg N, The human homologue of the yeast Prt1 protein is an integral part of the eukaryotic initiation factor 3 complex and interacts with p170, J. Biol. Chem. 272 (1997) 1110–1116. - PubMed
-
- Block KL, Vornlocher HP, Hershey JW, Characterization of cDNAs encoding the p44 and p35 subunits of human translation initiation factor eIF3, J. Biol. Chem. 273 (1998) 31901–31908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

