Brain injury in autonomic, emotional, and cognitive regulatory areas in patients with heart failure
- PMID: 19327623
- PMCID: PMC2730774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2008.10.020
Brain injury in autonomic, emotional, and cognitive regulatory areas in patients with heart failure
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is accompanied by autonomic, emotional, and cognitive deficits, indicating brain alterations. Reduced gray matter volume and isolated white matter infarcts occur in HF, but the extent of damage is unclear. Using magnetic resonance T2 relaxometry, we evaluated the extent of injury across the entire brain in HF.
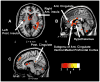
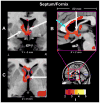
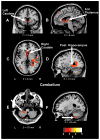
Methods and results: Proton-density and T2-weighted images were acquired from 13 HF (age 54.6 +/- 8.3 years; 69% male, left ventricular ejection fraction 0.28 +/- 0.07) and 49 controls (50.6 +/- 7.3 years, 59% male). Whole brain maps of T2 relaxation times were compared at each voxel between groups using analysis of covariance (covariates: age and gender). Higher T2 relaxation values, indicating injured brain areas (P < .005), emerged in sites that control autonomic, analgesic, emotional, and cognitive functions (hypothalamus, raphé magnus, cerebellar cortex, deep nuclei and vermis; temporal, parietal, prefrontal, occipital, insular, cingulate, and ventral frontal cortices; corpus callosum; anterior thalamus; caudate nuclei; anterior fornix and hippocampus). No brain areas showed higher T2 values in control vs. HF subjects.
Conclusions: Brain structural injury emerged in areas involved in autonomic, pain, mood, language, and cognitive function in HF patients. Comorbid conditions accompanying HF may result from neural injury associated with the syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fonarow GC, Yancy CW, Heywood JT. Adherence to heart failure quality-of-care indicators in US hospitals: analysis of the ADHERE Registry. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(13):1469–77. - PubMed
-
- Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2006;113(6):e85–151. - PubMed
-
- Cohn JN, Levine TB, Olivari MT, Garberg V, Lura D, Francis GS, et al. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1984;311(13):819–23. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey C, Harrison MB, Medves J, Tranmer JE. The symptom of pain with heart failure: a systematic review. J Card Fail. 2006;12(4):307–13. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey CM, Harrison MB, Friedberg E, Medves JM, Tranmer JE. The symptom of pain in individuals recently hospitalized for heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2007;22(5):368–74. discussion 6-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

