Genetic alteration of a bispecific ligand-directed toxin targeting human CD19 and CD22 receptors resulting in improved efficacy against systemic B cell malignancy
- PMID: 19327829
- PMCID: PMC2738628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.02.006
Genetic alteration of a bispecific ligand-directed toxin targeting human CD19 and CD22 receptors resulting in improved efficacy against systemic B cell malignancy
Abstract
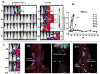
A bispecific ligand-directed toxin (BLT) called DT2219ARL consisting of two scFv ligands recognizing CD19 and CD22 and catalytic DT390 was genetically enhanced for superior in vivo anti-leukemia activity. Genetic alterations included reverse orienting VH-VL domains and adding aggregation reducing/stabilizing linkers. In vivo, these improvements resulted in previously unseen long-term tumor-free survivors measured in a bioluminescent xenograft imaging model in which the progression of human Raji Burkitt's lymphoma could be tracked in real time and in a Daudi model as well. Studies showed DT2219ARL was potent (IC50s 0.06-0.2 nM range) and selectively blockable. Imaging studies indicated the highly invasive nature of this B cell malignancy model and showed it likely induced pre-terminal hind limb paralysis because of metastasis to spinal regions prevented by DT2219ARL. DT2219ARL represents a new class of bispecific biological that can be continually improved by genetic mutation.
Figures






Comment in
-
Bispecific immunotoxins.Leuk Res. 2009 Sep;33(9):1173-4. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.03.037. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Leuk Res. 2009. PMID: 19406472 No abstract available.
References
-
- List AF. Role of multidrug resistance and its pharmacological modulation in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 1996;10:937–942. - PubMed
-
- Kreitman RJ. Recombinant fusion toxins for cancer treatment. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2002;2:785–91. - PubMed
-
- Goulet AC, Goldmacher VS, Lambert JM, Baron C, Roy DC, Kouassi E. Conjugation of blocked ricin to an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody increases antibody-induced cell calcium mobilization and CD19 internalization. Blood. 1997;90:2364–75. - PubMed
-
- Stone MJ, Sausville EA, Fay JW, et al. A phase I study of bolus versus continuous infusion of the anti-CD19 immunotoxin, IgG-HD37-dgA, in patients with B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1996;88:1188–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

