End-group effects on the properties of PEG-co-PGA hydrogels
- PMID: 19328754
- PMCID: PMC2708096
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.02.030
End-group effects on the properties of PEG-co-PGA hydrogels
Abstract
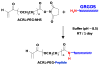
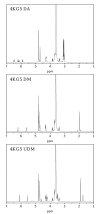
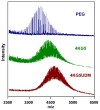
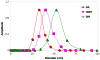
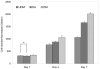
A series of resorbable poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(glycolic acid) (PEG-co-PGA, 4KG5) macromonomers have been synthesized with the chemistries from three different photopolymerizable end-groups (acrylates, methacrylates and urethane methacrylates). The aim of the study is to examine the effects of the chemistry of the cross-linker group on the properties of photocross-linked hydrogels. 4KG5 hydrogels were prepared by photopolymerization with high vinyl group conversion as confirmed by (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry using a 1D diffusion-ordered spectrometry pulse sequence. Our study reveals that the nature of end-groups in a moderately amphiphilic polymer can adjust the distribution and size of the micellar configuration in water, leading to changes in the macroscopic structure of hydrogels. By varying the chemistry of the cross-linker group (diacrylates (DA), dimethacrylates (DM) and urethane dimethacrylates (UDM)), we determined that the hydrophobicity of a single core polymer consisting of poly(glycolic acid) could be fine-tuned, leading to significant variations in the mechanical, swelling and degradation properties of the gels. In addition, the effects of cross-linker chemistry on cytotoxicity and proliferation were examined. Cytotoxicity assays showed that the three types of hydrogels (4KG5 DA, DM and UDM) were biocompatible and the introduction of RGD ligand enhanced cell adhesion. However, differences in gel properties and stability differentially affected the spreading and proliferation of myoblast C2C12 cells.
Figures






References
-
- Graham NB. Hydrogels: their future, Part I. Med Device Technol. 1998;9:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Graham NB. Hydrogels: their future, Part II. Med Device Technol. 1998;9(3):22–5. - PubMed
-
- Nair LS, Laurencin CT. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32:762–798.
-
- Zhang YL, Chu CC. The effect of molecular weight of biodegradable hydrogel components on indomethacin release from dextran and poly(DL)lactic acid based hydrogels. J Bio Comp Polym. 2002;17:65–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

