Identification of conserved regulatory elements in mammalian promoter regions: a case study using the PCK1 promoter
- PMID: 19329064
- PMCID: PMC5054123
- DOI: 10.1016/S1672-0229(09)60001-2
Identification of conserved regulatory elements in mammalian promoter regions: a case study using the PCK1 promoter
Abstract
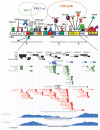
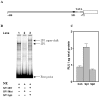
A systematic phylogenetic footprinting approach was performed to identify conserved transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) in mammalian promoter regions using human, mouse and rat sequence alignments. We found that the score distributions of most binding site models did not follow the Gaussian distribution required by many statistical methods. Therefore, we performed an empirical test to establish the optimal threshold for each model. We gauged our computational predictions by comparing with previously known TFBSs in the PCK1 gene promoter of the cytosolic isoform of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and achieved a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of approximately 32%. Almost all known sites overlapped with predicted sites, and several new putative TFBSs were also identified. We validated a predicted SP1 binding site in the control of PCK1 transcription using gel shift and reporter assays. Finally, we applied our computational approach to the prediction of putative TFBSs within the promoter regions of all available RefSeq genes. Our full set of TFBS predictions is freely available at http://bfgl.anri.barc.usda.gov/tfbsConsSites.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sp1 and AP2 enhance promoter activity of the mouse GM3-synthase gene.Gene. 2005 May 23;351:109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.03.010. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15890474
-
Regulation of KLF5 involves the Sp1 transcription factor in human epithelial cells.Gene. 2004 Apr 14;330:133-42. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.01.014. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15087132
-
Characterization of the human p11 promoter sequence.Gene. 2003 May 22;310:133-42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00529-8. Gene. 2003. PMID: 12801640
-
Identification of the promoter of human transcription factor Sp3 and evidence of the role of factors Sp1 and Sp3 in the expression of Sp3 protein.Gene. 2005 May 23;351:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.02.007. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15857802
-
Aspects of the control of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27031-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.040535. Epub 2009 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19636079 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
TransmiR v2.0: an updated transcription factor-microRNA regulation database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D253-D258. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30371815 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective review of the roles of multifunctional glucose-6-phosphatase in blood glucose homeostasis: Genesis of the tuning/retuning hypothesis.Life Sci. 2010 Sep 11;87(11-12):339-49. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.06.021. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20603134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine mapping for Weaver syndrome in Brown Swiss cattle and the identification of 41 concordant mutations across NRCAM, PNPLA8 and CTTNBP2.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059251. Epub 2013 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527149 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical RNA-DNA differences and other human genomic features are enriched within very short tandem repeats.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Jun 8;16(6):e1007968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007968. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32511223 Free PMC article.
-
MIRTFnet: analysis of miRNA regulated transcription factors.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022519. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins F.S. A vision for the future of genomics research. Nature. 2003;422:835–847. - PubMed
-
- Waterston R.H. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. - PubMed
-
- Lander E.S. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

