Identification of IRAK1 as a risk gene with critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 19329491
- PMCID: PMC2669395
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901181106
Identification of IRAK1 as a risk gene with critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
A combined forward and reverse genetic approach was undertaken to test the candidacy of IRAK1 (interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-1) as an X chromosome-encoded risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In studying approximately 5,000 subjects and healthy controls, 5 SNPs spanning the IRAK1 gene showed disease association (P values reaching 10(-10), odds ratio >1.5) in both adult- and childhood-onset SLE, in 4 different ethnic groups, with a 4 SNP haplotype (GGGG) being strongly associated with the disease. The functional role of IRAK1 was next examined by using congenic mouse models bearing the disease loci: Sle1 or Sle3. IRAK1 deficiency abrogated all lupus-associated phenotypes, including IgM and IgG autoantibodies, lymphocytic activation, and renal disease in both models. In addition, the absence of IRAK1 reversed the dendritic cell "hyperactivity" associated with Sle3. Collectively, the forward genetic studies in human SLE and the mechanistic studies in mouse models establish IRAK1 as a disease gene in lupus, capable of modulating at least 2 key checkpoints in disease development. This demonstration of an X chromosome gene as a disease susceptibility factor in human SLE raises the possibility that the gender difference in SLE may in part be attributed to sex chromosome genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


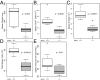

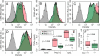
Comment in
-
Xq28 and lupus: IRAK1 or MECP2?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 16;106(24):E62; author reply E63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904068106. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19506310 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Russ V, Hochberg MC. In: Dubois' Lupus Erythematosus. Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002. pp. 65–83.
-
- Jacob CO, et al. Identification of novel susceptibility genes in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus using a uniquely designed candidate gene pathway platform. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:4164–4173. - PubMed
-
- Cassidy JT. In: Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. Cassidy JT, Petty RE, editors. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 1996. pp. 329–406.
-
- Lehman TJA. In: Dubois' Lupus Erythematosus. Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002. pp. 863–884. 4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR048095/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AR42460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI063622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI039824/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI24717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AR49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR48095/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR445650/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

