Targeted and genome-scale strategies reveal gene-body methylation signatures in human cells
- PMID: 19329998
- PMCID: PMC3566772
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1533
Targeted and genome-scale strategies reveal gene-body methylation signatures in human cells
Erratum in
- Nat Biotechnol. 2009 May;27(5):485
Abstract
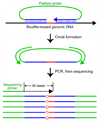
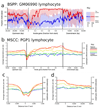
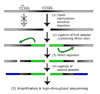
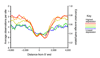
Studies of epigenetic modifications would benefit from improved methods for high-throughput methylation profiling. We introduce two complementary approaches that use next-generation sequencing technology to detect cytosine methylation. In the first method, we designed approximately 10,000 bisulfite padlock probes to profile approximately 7,000 CpG locations distributed over the ENCODE pilot project regions and applied them to human B-lymphocytes, fibroblasts and induced pluripotent stem cells. This unbiased choice of targets takes advantage of existing expression and chromatin immunoprecipitation data and enabled us to observe a pattern of low promoter methylation and high gene-body methylation in highly expressed genes. The second method, methyl-sensitive cut counting, generated nontargeted genome-scale data for approximately 1.4 million HpaII sites in the DNA of B-lymphocytes and confirmed that gene-body methylation in highly expressed genes is a consistent phenomenon throughout the human genome. Our observations highlight the usefulness of techniques that are not inherently or intentionally biased towards particular subsets like CpG islands or promoter regions.
Figures






Comment in
-
Locking in on the human methylome.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Apr;27(4):341-2. doi: 10.1038/nbt0409-341. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19352369 No abstract available.
References
-
- Suzuki MM, Bird A. DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:465–476. - PubMed
-
- Goll MG, Bestor TH. Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:481–514. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Jiang YH, Bressler J, Beaudet AL. Epigenetics and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2004;5:479–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

