House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells
- PMID: 19330007
- PMCID: PMC2789255
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1946
House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells
Abstract
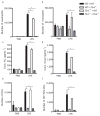
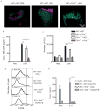
Barrier epithelial cells and airway dendritic cells (DCs) make up the first line of defense against inhaled substances such as house dust mite (HDM) allergen and endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide, LPS). We hypothesized that these cells need to communicate with each other to cause allergic disease. We show in irradiated chimeric mice that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression on radioresistant lung structural cells, but not on DCs, is necessary and sufficient for DC activation in the lung and for priming of effector T helper responses to HDM. TLR4 triggering on structural cells caused production of the innate proallergic cytokines thymic stromal lymphopoietin, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-25 and interleukin-33. The absence of TLR4 on structural cells, but not on hematopoietic cells, abolished HDM-driven allergic airway inflammation. Finally, inhalation of a TLR4 antagonist to target exposed epithelial cells suppressed the salient features of asthma, including bronchial hyperreactivity. Our data identify an innate immune function of airway epithelial cells that drives allergic inflammation via activation of mucosal DCs.
Figures




Comment in
-
Dust mites' dirty dealings in the lung.Nat Med. 2009 Apr;15(4):366-7. doi: 10.1038/nm0409-366. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19350005 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barnes PJ. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler SF, Liu YJ. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin in normal and pathogenic T cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:709–714. - PubMed
-
- Sha Q, et al. Activation of airway epithelial cells by toll-like receptor agonists. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004;31:358–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

