Flecainide prevents catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in mice and humans
- PMID: 19330009
- PMCID: PMC2904954
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1942
Flecainide prevents catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in mice and humans
Abstract
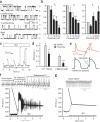
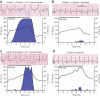
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a potentially lethal inherited arrhythmia syndrome in which drug therapy is often ineffective. We discovered that flecainide prevents arrhythmias in a mouse model of CPVT by inhibiting cardiac ryanodine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) release and thereby directly targeting the underlying molecular defect. Flecainide completely prevented CPVT in two human subjects who had remained highly symptomatic on conventional drug therapy, indicating that this currently available drug is a promising mechanism-based therapy for CPVT.
Figures
References
-
- Leenhardt A, et al. Circulation. 1995;91:1512–1519. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed U, Gollob MH, Gow RM, Krahn AD. Heart Rhythm. 2006;3:1486–1489. - PubMed
-
- Pizzale S, Gollob MH, Gow R, Birnie DH. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008;9:1319–1321. - PubMed
-
- Wilde AA, et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:2024–2029. - PubMed
-
- Robinson M, Park J, Raff G. Heart Rhythm. 2007;4(Suppl):S100.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

