Kinetics and pharmacology of the D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors in Japanese quail brain
- PMID: 19330447
- PMCID: PMC11506156
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9382-6
Kinetics and pharmacology of the D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors in Japanese quail brain
Abstract
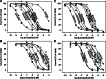
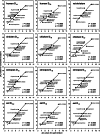
Although the avian brain dopamine system and its functions have been studied much less than the mammalian one, there is an increasing interest in the role of dopamine and its receptors in a wide variety of motor, cognitive and emotional functions in birds with implications for basic research, medicine or agriculture. Pharmacological characterisation of the avian dopamine receptors has had little attention. In this paper we characterise the two classes of dopamine receptors in Japanese quail brain by radioligand binding techniques using [(3)H]SCH 23390 (D(1)) and [(3)H]spiperone (D(2)). Association, dissociation and saturation analyses showed that the binding of both radioligands is time- and concentration-dependent, saturable and reversible. Apparent dissociation constants determined for [(3)H]SCH 23390 and [(3)H]spiperone from concentration isotherms were 1.07 and 0.302 nM and the maximum binding capacities were 89.3 and 389.3 fmol per mg of protein, respectively. Using competitive binding studies with a spectrum of dopamine and other neurotransmitter receptor agonists/antagonists, the [(3)H]SCH 23390 and [(3)H]spiperone binding sites were characterised pharmacologically. Pharmacological profiles of quail dopamine receptors showed a high degree of pharmacological homology with other vertebrate dopamine receptors. The data presented extend the knowledge of kinetics and pharmacology of D(1)- and D(2)-like dopamine receptors in birds, provide data for avian psychopharmacological and comparative studies and represent an important complement to studies using cell expression systems.
Figures


References
-
- Acerbo MJ, Výboh P, Košťál Ľ, Kubíková Ľ, Delius JD (2005) Repeated apomorphine administration alters dopamine D1 and D2 receptor densities in pigeon basal telencephalon. Exp Brain Res 160:533–537. doi:10.1007/s00221-004-2158-9 - PubMed
-
- Andersen PH, Grønvald FC, Jansen JA (1985) A comparison between dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase and 3H-SCH 23390 binding in rat striatum. Life Sci 37:1971–1983. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(85)90028-1 - PubMed
-
- Baillien M, Balthazart J (1997) A direct dopaminergic control of aromatase activity in the quail preoptic area. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 63:99–113. doi:10.1016/S0960-0760(97)00080-0 - PubMed
-
- Bálint E, Csillag A (2007) Nucleus accumbens subregions: homological and immunohistochemical study in the domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Cell Tissue Res 327:221–230. doi:10.1007/s00441-006-0295-0 - PubMed
-
- Ball GF, Casto JM, Balthazart J (1995) Autoradiographic localization of D1-like dopamine receptors in the forebrain of male and female Japanese quail and their relationship with immunoreactive tyrosine hydroxylase. J Chem Neuroanat 9:121–133. doi:10.1016/0891-0618(95)00075-I - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

