Dopamine modulates effort-based decision making in rats
- PMID: 19331447
- PMCID: PMC2791340
- DOI: 10.1037/a0014625
Dopamine modulates effort-based decision making in rats
Abstract
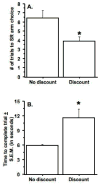
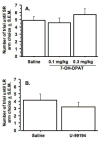
Previous research has implicated dopamine as a modulating factor in choice behavior based on effort. The purpose of the present study was to determine the individual contribution of different dopamine receptors to effort-based decision making in rats. Rats were trained in a T-maze to choose a large-reward arm that contained 8 pellets of food over a small-reward arm that contained 2 pellets of food. The rats then were trained to climb progressively higher barriers to obtain the food from the large-reward arm. Using a discounting procedure on each test day, it was found that rats were more likely to choose the small-reward arm after treatment with the D1 antagonist, SCH-23390, or the D2 antagonist, haloperidol. The dopamine agonist, D-amphetamine, biased the rats toward choosing the large-reward arm and blunted the effects of SCH-23390 or haloperidol. Treatment with the D3 receptor antagonist, U99194, or the D3 receptor agonist, 7-OH-DPAT, did not alter choice behavior. These data indicate that D1 and D2 receptors are required for decisions based on effort.
(c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Dopamine, effort, and decision making: theoretical comment on Bardgett et al. (2009).Behav Neurosci. 2009 Apr;123(2):463-7. doi: 10.1037/a0015381. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19331471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnt J. Differential effects of classical and newer antipsychotics on the hypermotility induced by two dose levels of D-amphetamine. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1995;283:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Audinot V, Newman-Tancredi A, Gobert A, Rivet JM, Brocco M, Lejeune F, Gluck L, Desposte I, Bervoets K, Dekeyne A, Millan MJ. A comparative in vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonists (+)-S 14297, nafadotride, GR 103,691 and U 99194. Journal of Pharmacological and Experimental Therapeutics. 1998;287:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Bardgett ME, Henry JD. Locomotor activity and accumbens Fos expression driven by ventral hippocampal stimulation require D1 and D2 receptors. Neuroscience. 1999;94:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Bardgett ME, Jackson JL, Taylor BM, Csernansky JG. The effects of kainic acid lesions on locomotor responses to haloperidol and clozapine. Psychopharmacology. 1998;135:270–278. - PubMed
-
- Cardinal RN. Neural systems implicated in delayed and probabilistic reinforcement. Neural Networks. 2006;19:1277–1301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

