Nicotine deprivation and trait impulsivity affect smokers' performance on cognitive tasks of inhibition and attention
- PMID: 19331485
- PMCID: PMC2863308
- DOI: 10.1037/a0015657
Nicotine deprivation and trait impulsivity affect smokers' performance on cognitive tasks of inhibition and attention
Abstract
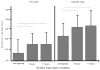
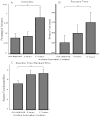
Increased nicotine deprivation and impulsivity have been associated with relapse but the degree to which they together influence cognitive processing has not been explored. We examined the effects of increasing levels of nicotine deprivation on cognitive processing, and assessed the relationship of trait impulsivity with these effects in daily smokers (n=30). Using a within-subject design with three deprivation conditions (nondeprived, 5-hr, 17-hr), volunteers completed the Conners' Continuous Performance Task-II and the Cued Go/No-Go Task. Trait impulsivity was assessed at intake with the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (Patton et al., 1995). Mixed-model regression analyses revealed deprivation slowed reaction time, increased errors, increased variability in responding, and increased failures of inhibitory control. Performance at 17 hours of deprivation was most likely to be affected. Significant deprivation and impulsivity interactions indicated impulsiveness was negatively correlated with deprivation-associated performance decrements. Less impulsive smokers were more affected by deprivation, demonstrating greater impairment. Research is needed to understand mechanisms by which impulsivity confers greater risk for relapse. Our results suggest deprivation may not increase relapse risk among impulsive smokers by increasing impairment of cognitive processing.
Copyright (c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is impulsivity related to attentional bias in cigarette smokers? An exploration across levels of nicotine dependency and deprivation.Behav Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 1;35(4):172-184. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000775. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Behav Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38651685
-
The effects of varying cigarette deprivation duration on cognitive and performance tasks.J Subst Abuse. 1989;1(4):407-16. J Subst Abuse. 1989. PMID: 2485288
-
Efficacy of a nicotine (4 mg)-containing lozenge on the cognitive impairment of nicotine withdrawal.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008 Dec;28(6):667-74. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31818c9bb8. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19011436 Clinical Trial.
-
Measuring impulsivity and modeling its association with cigarette smoking.Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev. 2004 Dec;3(4):261-75. doi: 10.1177/1534582305276838. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev. 2004. PMID: 15812110 Review.
-
Effects of the nicotine patch on performance during the first week of smoking cessation.Nicotine Tob Res. 2003 Apr;5(2):169-80. doi: 10.1080/1462220031000074873. Nicotine Tob Res. 2003. PMID: 12745489 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurogenetics and Epigenetics in Impulsive Behaviour: Impact on Reward Circuitry.J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2012 May 30;3(3):1000115. doi: 10.4172/2157-7412.1000115. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 23264884 Free PMC article.
-
Length of smoking deprivation moderates the effects of alcohol administration on urge to smoke.Addict Behav. 2014 May;39(5):976-9. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.01.023. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24556154 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trait differences in response to chronic nicotine and nicotine withdrawal in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Feb;231(3):567-80. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3270-y. Epub 2013 Sep 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24037510
-
Neural correlates of performance monitoring in daily and intermittent smokers.Clin Neurophysiol. 2014 Jul;125(7):1417-26. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24380760 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of varenicline and bupropion on cognitive processes among nicotine-deprived smokers.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Feb;20(1):63-70. doi: 10.1037/a0025594. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21942262 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- al’Absi M, Amunrud T, Wittmers LE. Psychophysiological effects of nicotine abstinence and behavioral challenges in habitual smokers. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 2002;72:707–716. - PubMed
-
- American Psychological Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM–IV–TR. 4 2000.
-
- Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC. Addiction motivation reformulated: An affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychological Review. 2004;111:33–51. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister RF. Ego depletion and self-regulation failure: A resource model of self-control. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2003;27:281–284. - PubMed
-
- Bell SL, Taylor RC, Singleton EG, Henningfield JE, Heishman SJ. Smoking after nicotine deprivation enhances cognitive performance and decreases tobacco craving in drug abusers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 1999;1:45–52. - PubMed

