Horizontal cell feedback regulates calcium currents and intracellular calcium levels in rod photoreceptors of salamander and mouse retina
- PMID: 19332495
- PMCID: PMC2697303
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.169656
Horizontal cell feedback regulates calcium currents and intracellular calcium levels in rod photoreceptors of salamander and mouse retina
Abstract
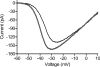
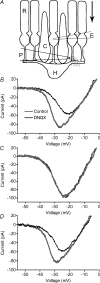
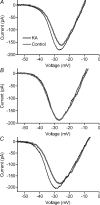
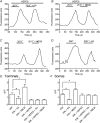
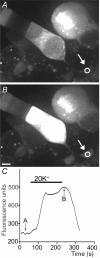
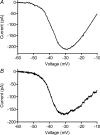
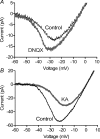
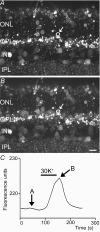
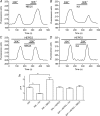
We tested whether horizontal cells (HCs) provide feedback that regulates the Ca(2+) current (I(Ca)) of rods in salamander and mouse retinas. In both species, hyperpolarizing HCs by puffing a glutamate antagonist, 6,7-dinitro-quinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX), onto HC processes caused a negative shift in the voltage dependence of rod I(Ca) and increased its peak amplitude. Conversely, depolarizing HCs by puffing kainic acid (KA) into the outer plexiform layer (OPL) caused a positive voltage shift and decreased rod I(Ca.) Experiments on salamander retina showed that these effects were blocked by addition of the pH buffer, Hepes. Intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) was examined in rods by confocal microscopy after loading salamander and mouse retinal slices with Fluo-4. Rods were depolarized to near the dark resting potential by bath application of high K(+) solutions. Hyperpolarizing HCs with 2,3-dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulphamoylbenzo[f]quinoxaline (NBQX) enhanced high K(+)-evoked Ca(2+) increases whereas depolarizing HCs with KA inhibited Ca(2+) increases. In both species these effects of NBQX and KA were blocked by addition of Hepes. Thus, like HC feedback in cones, changes in HC membrane potential modulate rod I(Ca) thereby regulating rod [Ca(2+)](i) at physiological voltages, in both mouse and salamander retinas. By countering the reduced synaptic output that accompanies hyperpolarization of rods to light, HC feedback will subtract spatially averaged luminance levels from the responses of individual rods to local changes. The finding that HC to rod feedback is present in both amphibian and mammalian species shows that this mechanism is highly conserved across vertebrate retinas.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

