N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate the phosphorylation and desensitization of muscarinic receptors in cerebellar granule neurons
- PMID: 19332541
- PMCID: PMC2719353
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M901031200
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate the phosphorylation and desensitization of muscarinic receptors in cerebellar granule neurons
Abstract
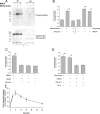
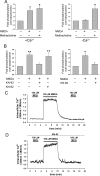
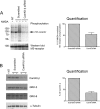
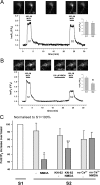
Changes in synaptic strength mediated by ionotropic glutamate N-methyl-D-asparate (NMDA) receptors is generally considered to be the molecular mechanism underlying memory and learning. NMDA receptors themselves are subject to regulation through signaling pathways that are activated by G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). In this study we investigate the ability of NMDA receptors to regulate the signaling of GPCRs by focusing on the G(q/11)-coupled M(3)-muscarinic receptor expressed endogenously in mouse cerebellar granule neurons. We show that NMDA receptor activation results in the phosphorylation and desensitization of M(3)-muscarinic receptors through a mechanism dependent on NMDA-mediated calcium influx and the activity of calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Our study reveals a complex pattern of regulation where GPCRs (M(3)-muscarinic) and NMDA receptors can feedback on each other in a process that is likely to influence the threshold value of signaling networks involved in synaptic plasticity.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

