Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L Is a subunit of human KMT3a/Set2 complex required for H3 Lys-36 trimethylation activity in vivo
- PMID: 19332550
- PMCID: PMC2708867
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808431200
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L Is a subunit of human KMT3a/Set2 complex required for H3 Lys-36 trimethylation activity in vivo
Abstract
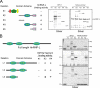
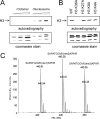
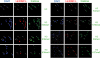
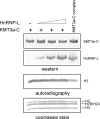
The presence of histone H3 lysine 36 methylation (H3K36me) correlates with actively transcribed genes. In yeast, histone H3K36me mediated by KMT3 (also known as Set2) recruits a histone deacetylase complex, Rpd3s, to ensure the fidelity of transcription initiation. We report the purification of human KMT3a (also known as HYPB or hSet2) complex and the identification of a novel, higher eukaryotic specific subunit, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (HnRNP-L). Interestingly, although KMT3a has intrinsic activity in vitro, HnRNP-L is essential in vivo. Moreover, KMT3a generates mono-, di-, and trimethylated products in vitro, but RNA interference against KMT3a or HnRNP-L down-regulates exclusively the H3K36me3 mark in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Jenuwein T., Allis C. D. ( 2001) Science 293, 1074– 1080 - PubMed
-
- Margueron R., Trojer P., Reinberg D. ( 2005) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 15, 163– 176 - PubMed
-
- Martin C., Zhang Y. ( 2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 838– 849 - PubMed
-
- Li B., Carey M., Workman J. L. ( 2007) Cell 128, 707– 719 - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. ( 2007) Cell 128, 693– 705 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

