Fluorescence changes reveal kinetic steps of muscarinic receptor-mediated modulation of phosphoinositides and Kv7.2/7.3 K+ channels
- PMID: 19332618
- PMCID: PMC2699104
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200810075
Fluorescence changes reveal kinetic steps of muscarinic receptor-mediated modulation of phosphoinositides and Kv7.2/7.3 K+ channels
Abstract
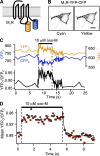
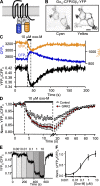
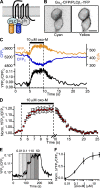
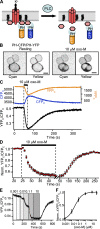
G protein-coupled receptors initiate signaling cascades. M(1) muscarinic receptor (M(1)R) activation couples through Galpha(q) to stimulate phospholipase C (PLC), which cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)). Depletion of PIP(2) closes PIP(2)-requiring Kv7.2/7.3 potassium channels (M current), thereby increasing neuronal excitability. This modulation of M current is relatively slow (6.4 s to reach within 1/e of the steady-state value). To identify the rate-limiting steps, we investigated the kinetics of each step using pairwise optical interactions likely to represent fluorescence resonance energy transfer for M(1)R activation, M(1)R/Gbeta interaction, Galpha(q)/Gbeta separation, Galpha(q)/PLC interaction, and PIP(2) hydrolysis. Electrophysiology was used to monitor channel closure. Time constants for M(1)R activation (<100 ms) and M(1)R/Gbeta interaction (200 ms) are both fast, suggesting that neither of them is rate limiting during muscarinic suppression of M current. Galpha(q)/Gbeta separation and Galpha(q)/PLC interaction have intermediate 1/e times (2.9 and 1.7 s, respectively), and PIP(2) hydrolysis (6.7 s) occurs on the timescale of M current suppression. Overexpression of PLC accelerates the rate of M current suppression threefold (to 2.0 s) to become nearly contemporaneous with Galpha(q)/PLC interaction. Evidently, channel release of PIP(2) and closure are rapid, and the availability of active PLC limits the rate of M current suppression.
Figures


References
-
- Biddlecome G.H., Berstein G., Ross E.M. 1996. Regulation of phospholipase C-β1 by Gq and m1 muscarinic cholinergic receptor. Steady-state balance of receptor-mediated activation and GTPase-activating protein-promoted deactivation.J. Biol. Chem. 271:7999–8007 - PubMed
-
- Brown D.A. 1983. Slow cholinergic excitation—a mechanism for increasing neuronal excitability.Trends Neurosci. 6:302–307
-
- Brown D.A., Adams P.R. 1980. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone.Nature. 283:673–676 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

