Edema control by cediranib, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted kinase inhibitor, prolongs survival despite persistent brain tumor growth in mice
- PMID: 19332720
- PMCID: PMC2739611
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.9356
Edema control by cediranib, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted kinase inhibitor, prolongs survival despite persistent brain tumor growth in mice
Abstract
Purpose: Recent clinical trials of antivascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents for glioblastoma showed promising progression-free and overall survival rates. However, available clinical imaging does not separate antitumor effects from antipermeability effects of these agents. Thus although anti-VEGF agents may decrease tumor contrast-enhancement, vascularity, and edema, the mechanisms leading to improved survival in patients remain incompletely understood. Our goal was to determine whether alleviation of edema by anti-VEGF agents alone could increase survival in mice.
Methods: We treated mice bearing three different orthotopic models of glioblastoma with a VEGF-targeted kinase inhibitor, cediranib. Using intravital microscopy, molecular techniques, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), we measured survival, tumor growth, edema, vascular morphology and function, cancer cell apoptosis and proliferation, and circulating angiogenic biomarkers.
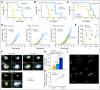
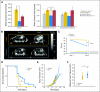
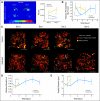
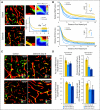
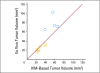
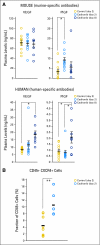
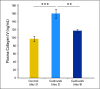
Results: We show by intravital microscopy that cediranib significantly decreased tumor vessel permeability and diameter. Moreover, cediranib treatment induced normalization of perivascular cell coverage and thinning of the basement membrane, as mirrored by an increase in plasma collagen IV. These rapid changes in tumor vascular morphology and function led to edema alleviation -- as measured by MRI and by dry/wet weight measurement of water content -- but did not affect tumor growth. By immunohistochemistry, we found a transient decrease in macrophage infiltration and significant but minor changes in tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis. Systemically, cediranib increased plasma VEGF and placenta growth factor levels, and the number of circulating CXCR4(+)CD45(+) cells. However, by controlling edema, cediranib significantly increased survival of mice in the face of persistent tumor growth.
Conclusion: Anti-VEGF agents may be able to improve survival of patients with glioblastoma, even without inhibiting tumor growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Cloughesy TF. A phase II, randomized, non-comparative clinical trial of the effect of bevacizumab (BV) alone or in combination with irinotecan (CPT) on 6-month progression free survival (PFS6) in recurrent, treatment-refractory glioblastoma (GBM) J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(suppl):91s. abstr 2010b.
-
- Pope WB, Lai A, Nghiemphu P, et al. MRI in patients with high-grade gliomas treated with bevacizumab and chemotherapy. Neurology. 2006;66:1258–1260. - PubMed
-
- Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE, 2nd, et al. Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1253–1259. - PubMed
-
- Norden AD, Young GS, Setayesh K, et al. Bevacizumab for recurrent malignant gliomas: Efficacy, toxicity, and patterns of recurrence. Neurology. 2008;70:779–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA073479/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA80124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA080124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA129371/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24-CA125440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA096915/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129371/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA125440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 AG029415/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA115767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

