MET pathway as a therapeutic target
- PMID: 19333071
- PMCID: PMC2664527
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31819d6f91
MET pathway as a therapeutic target
Abstract
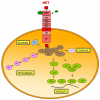
Dysregulation of mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor receptor tyrosine kinase pathway leads to cell proliferation, protection from apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. It can be dysregulated through overexpression, constitutive activation, gene amplification, ligand-dependent activation or mutation. New drugs targeting various mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor pathways are being investigated with promising results.
Figures
References
-
- Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF, Aaronson SA. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991;251:802–804. - PubMed
-
- Di Renzo MF, Narsimhan RP, Olivero M, Bretti S, Giordano S, Medico E, Gaglia P, Zara P, Comoglio PM. Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene. 1991;6:1997–2003. - PubMed
-
- Benvenuti S, Comoglio PM. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase in invasion and metastasis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:316–325. - PubMed
-
- Sattler M, Salgia R. c-Met and hepatocyte growth factor: potential as novel targets in cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep. 2007;9:102–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

