Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a new target for cardioprotection
- PMID: 19333883
- PMCID: PMC2900160
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a new target for cardioprotection
Abstract
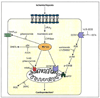
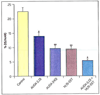
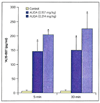
Arachidonic acid is metabolized to a number of bioactive eicosanoid molecules by several enzymes, including enzymes of the COX, lipoxygenase and cytochrome P450 (CYP) monooxygenase pathways. Inhibition of the CYP omega-hydroxylase pathway, stimulation of the CYP-epoxygenase pathway and administration of exogenous epoxyeicosatrienoic acids resulted in cardioprotection in animal models of ischemia; contractile function was improved in mouse hearts subjected to global ischemia/reperfusion, and infarct size was reduced in canine and rat hearts. Cardioprotective effects were also achieved when metabolism of the endogenous epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) by their major enzymatic hydrolysis pathway was blocked in gene knockout mice (EPHX2-/-) or by inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), such as 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid (AUDA). Pretreatment of canine hearts with AUDA dose-dependently reduced infarct size, and AUDA enhanced the infarct-sparing effect of treatment with exogenous EETs. The preliminary results of studies in rodent hearts have also demonstrated that AUDA and AUDA-butyl ester reduce infarct size. These results and others obtained in models of myocardial stunning and hypertrophy suggest that inhibitors of EPHX2 or sEH have therapeutic potential in a broad range of cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
References
-
-
Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2007 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115(5):e69–e171. • An excellent summary of the demographics of CVD in the US.
-
-
-
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KB. Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1124–1136. • The first paper to describe the phenomenon of IPC and the consequent reduction in infarct size in dogs.
-
-
-
zhao zQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, Wang NP, Guyton RA, Vinten-Johansen J. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: Comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(2):H579–H588. • The first paper to describe the phenomenon of ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion and compare its efficacy with that of ischemic IPC.
-
-
-
Spector AA, Norris AW. Action of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cellular function. Am J Physiol Ceil Physiol. 2007;292(3):C996–C1012. • A thorough review of the cellular actions of the EETS in different organs.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
