Wnt signaling as a therapeutic target for bone diseases
- PMID: 19335070
- PMCID: PMC3023986
- DOI: 10.1517/14728220902841961
Wnt signaling as a therapeutic target for bone diseases
Abstract
Background: There is a need to develop new bone anabolic agents because current bone regeneration regimens have limitations. The Wingless-type MMTV integration site (Wnt) pathway has emerged as a regulator of bone formation and regeneration.
Objective: To review the molecular basis for Wnt pathway modulation and discuss strategies that target it and improve bone mass.
Methods: Data in peer-reviewed reports and meeting abstracts are discussed.
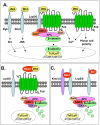
Results/conclusions: Neutralizing inhibitors of Wnt signaling have emerged as promising strategies. Small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta increase bone mass, lower adiposity and reduce fracture risk. Neutralizing antibodies to Dickkopf 1, secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 and sclerostin produce similar outcomes in animal models. These drugs are exciting breakthroughs but are not without risks. The challenges include tissue-specific targeting and consequently, long-term safety.
Figures

References
-
- Dennison E, Mohamed MA, Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006;32(4):617–29. - PubMed
-
- United States Department of Health and Human Services . Bone health and osteoporosis: A report of the surgeon general. U.S. Department of Health and Human Servises, Office of the Surgeon General; Rockville, MD: 2004.
-
- Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: Principal results from the women's health initiative randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2002;288(3):321–33. - PubMed
-
- Vahle JL, Sato M, Long GG, et al. Skeletal changes in rats given daily subcutaneous injections of recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1–34) for 2 years and relevance to human safety. Toxicol Pathol. 2002;30(3):312–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
