A novel protein complex in membrane rafts linking the NR2B glutamate receptor and autophagy is disrupted following traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 19335206
- PMCID: PMC2848823
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2008.0783
A novel protein complex in membrane rafts linking the NR2B glutamate receptor and autophagy is disrupted following traumatic brain injury
Abstract
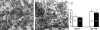
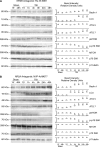
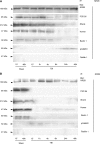
Hyperactivation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NRs) is associated with neuronal cell death induced by traumatic brain injury (TBI) and many neurodegenerative conditions. NR signaling efficiency is dependent on receptor localization in membrane raft microdomains. Recently, excitotoxicity has been linked to autophagy, but mechanisms governing signal transduction remain unclear. Here we have identified protein interactions between NR2B signaling intermediates and the autophagic protein Beclin-1 in membrane rafts of the normal rat cerebral cortex. Moderate TBI induced rapid recruitment and association of NR2B and pCaMKII to membrane rafts, and translocation of Beclin-1 out of membrane microdomains. Furthermore, TBI caused significant increases in expression of key autophagic proteins and morphological hallmarks of autophagy that were significantly attenuated by treatment with the NR2B antagonist Ro 25-6981. Thus, stimulation of autophagy by NR2B signaling may be regulated by redistribution of Beclin-1 in membrane rafts after TBI.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and its signaling intermediates are recruited to lipid rafts in the traumatized brain.J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 8;24(49):11010-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3823-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15590916 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy is activated and might protect neurons from degeneration after traumatic brain injury.Neurosci Bull. 2008 Jun;24(3):143-9. doi: 10.1007/s12264-008-1108-0. Neurosci Bull. 2008. PMID: 18500386 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of lovastatin on learning and memory deficits caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia-hypercapnia: through regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptor-ERK pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 9;9(4):e94278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094278. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24718106 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect of estrogen: role of nonsynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA receptors.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Apr;93:27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23085545 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia activation as a biomarker for traumatic brain injury.Front Neurol. 2013 Mar 26;4:30. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2013.00030. eCollection 2013. Front Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23531681 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Cathepsin D and Beclin-1 mRNA and protein expression by the excitotoxin quinolinic acid in human astrocytes and neurons.Metab Brain Dis. 2014 Sep;29(3):873-83. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9557-9. Epub 2014 May 16. Metab Brain Dis. 2014. Retraction in: Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Aug;38(6):2197. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01241-3. PMID: 24833554 Retracted.
-
Revisiting Traumatic Brain Injury: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Interventions.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 29;8(10):389. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100389. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33003373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoflurane/nitrous oxide anesthesia induces increases in NMDA receptor subunit NR2B protein expression in the aged rat brain.Brain Res. 2012 Jan 11;1431:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22137658 Free PMC article.
-
Previous physical exercise alters the hepatic profile of oxidative-inflammatory status and limits the secondary brain damage induced by severe traumatic brain injury in rats.J Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;595(17):6023-6044. doi: 10.1113/JP273933. Epub 2017 Jul 30. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28726269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarts M.M. Tymianski M. Molecular mechanisms underlying specificity of excitotoxic signaling in neurons. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004;4:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Abulrob A. Tauskela J.S. Mealing G. Brunette E. Faid K. Stanimirovic D. Protection by cholesterol-extracting cyclodextrins: a role for N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor redistribution. J. Neurochem. 2005;92:1477–1486. - PubMed
-
- Arundine M. Chopra G.K. Wrong A. Lei S. Aarts M.M. MacDonald J.F. Tymianski M. Enhanced vulnerability to NMDA toxicity in sublethal traumatic neuronal injury in vitro. J. Neurotrauma. 2003;20:1377–1395. - PubMed
-
- Baehrecke E.H. Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nat. Rev. 2005;6:505–510. - PubMed
-
- Barria A. Malinow R. NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron. 2005;48:289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

