Effects of surfactant protein-A on the interaction of Pneumocystis murina with its host at different stages of the infection in mice
- PMID: 19335775
- PMCID: PMC2675919
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2008.00363.x
Effects of surfactant protein-A on the interaction of Pneumocystis murina with its host at different stages of the infection in mice
Abstract
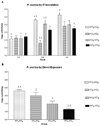
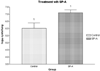
We examined the effects of surfactant protein A (SP-A), a collectin, on the interaction of Pneumocystis murina with its host at the beginning, early to middle, and late stages of infection. Pneumocystis murina from SP-A wild-type (WT) mice inoculated intractracheally into WT mice (WT(S)-WT(R)) adhered well to alveolar macrophages, whereas organisms from SP-A knockout (KO) mice inoculated into KO mice (KO(S)-KO(R)) did not. Substitution of WT mice as the source of organisms (WT(S)-KO(R)) or recipient host macrophages (KO(S)-WT(R)) restored adherence to that found with WT(S)-WT(R) mice. In contrast, when immunosuppressed KO and WT mice were inoculated with P. murina from a homologous source (KO(S)-KO(R), WT(S)-WT(R)) or heterologous source (WT(S)-KO(R), KO(S)-WT(R)) and followed sequentially, WT(S)-KO(R) mice had the highest levels of infection at weeks 3 and 4; these mice also had the highest levels of the chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and neutrophils in lavage fluid at week 3. Surfactant protein-A administered to immunosuppressed KO(S)-KO(R) mice with Pneumocystis pneumonia for 8 wk as a therapeutic agent failed to lower the organism burden. We conclude that SP-A can correct the host immune defect in the beginning of P. murina infection, but not in the middle or late stages of the infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pneumocystis murina colonization in immunocompetent surfactant protein A deficient mice following environmental exposure.Respir Res. 2009 Feb 19;10(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-10. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19228388 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant protein A limits Pneumocystis murina infection in immunosuppressed C3H/HeN mice and modulates host response during infection.Microbes Infect. 2005 Apr;7(4):748-59. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.01.011. Epub 2005 Mar 22. Microbes Infect. 2005. PMID: 15857803
-
Efficient resolution of Pneumocystis murina infection in surfactant protein A-deficient mice following withdrawal of corticosteroid-induced immunosuppression.J Med Microbiol. 2006 Feb;55(Pt 2):143-147. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46190-0. J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16434705
-
Immune reconstitution during Pneumocystis lung infection: disruption of surfactant component expression and function by S-nitrosylation.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2277-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802775. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19201882 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophage and glycoprotein responses to Pneumocystis carinii.Semin Respir Infect. 1998 Dec;13(4):339-47. Semin Respir Infect. 1998. PMID: 9872631 Review.
Cited by
-
Transmission and Colonization of Pneumocystis jirovecii.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;7(11):979. doi: 10.3390/jof7110979. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo rescue of alveolar macrophages from SP-A knockout mice with exogenous SP-A nearly restores a wild type intracellular proteome; actin involvement.Proteome Sci. 2011 Oct 28;9:67. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-9-67. Proteome Sci. 2011. PMID: 22035134 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction of Human Pathogenic Fungi With C-Type Lectin Receptors.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1261. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01261. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumocystis Pneumonia: Pitfalls and Hindrances to Establishing a Reliable Animal Model.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;8(2):129. doi: 10.3390/jof8020129. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alcorn JF, Wright JR. Surfactant protein A inhibits alveolar macrophage cytokine production by CD14-independent pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004;286:L129–L136. - PubMed
-
- Atochina EN, Beck JM, Preston AM, Haczku A, Tomer Y, Scanlon ST, Fusaro T, Casey J, Hawgood S, Gow AJ, Beers MF. Enhanced lung injury and delayed clearance of Pneumocystis carinii in surfactant protein A-deficient mice: attenuation of cytokine responses and reactive oxygen-nitrogen species. Infect. Immun. 2004a;72:6002–6011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atochina EN, Gow AJ, Beck JM, Haczku A, Inch A, Kadire H, Tomer Y, Davis C, Preston AM, Poulain F, Beers MF. Delayed clearance of Pneumocystis carinii infection, increased inflammation, and altered nitric oxide metabolism in lungs of surfactant protein-D knockout mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2004b;189:1528–1539. - PubMed
-
- Benfield TJ, Kharazmi A, Larsen CG, Lundgren JD. Neutrophil chemotactic activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with AIDS-associated Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1997;29:367–371. - PubMed
-
- Blau H, Riklis S, Van Iwaarden JF, McCormack FX, Kalina M. Nitric oxide production by rat alveolar macrophages can be modulated in vitro by surfactant protein A. Am. J Physiol. 1997;272:L1198–L1204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

